Figure 1.
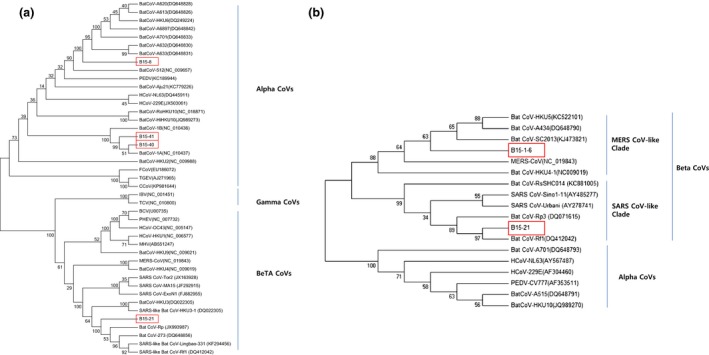
Phylogenetic trees constructed from bat coronavirus sequences detected in this study and from other coronaviruses. (a) bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1000 replicates with the UPGMA method (evolutionary distance parameter: maximum composite likelihood method) based on 351 bases of the RNA‐dependent RNA polymerase gene, (b) bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1000 replicates using the neighbour‐joining method (evolutionary distance parameter: maximum composite likelihood method) based on 163 bases of the spike gene. The box indicates the bat CoV sequences obtained in this study.
