Figure 1.
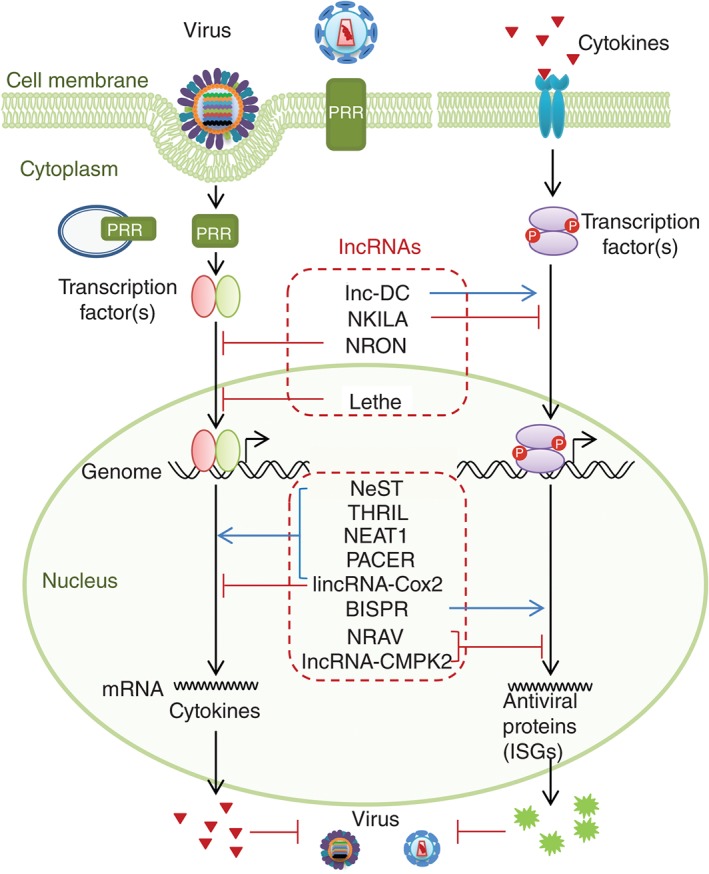
Host lncRNAs regulate multiple steps of the antiviral innate immune response. Upon viral invasion, host cell starts the PRR signaling cascade, which further activates the transcription factors and initiates the expression of cytokines. After binding with corresponding receptors, cytokines trigger the receptor‐associated signaling and the production of antiviral proteins, such as ISG proteins. Some cytoplasmic or nuclear lncRNAs can increase or inhibit the activities of transcription factors, which are listed in the upper dashed red rectangle. Other nuclear lncRNAs can modulate the transcription of cytokines or antiviral genes (ISGs), which are listed in the lower dashed red rectangle.
