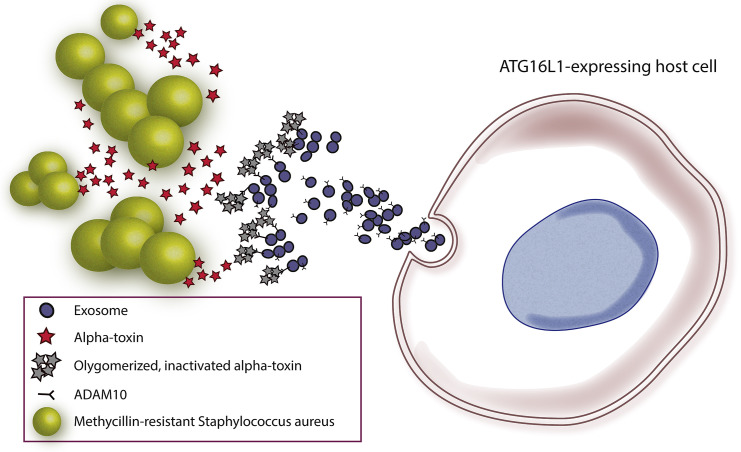
Figure 1.
ATG16L1-Expressing Cells Release Exosomes that Neutralize S. aureus Alpha-Toxin
Upon exposure to S. aureus, ATG16L1-expressing cells release large amounts of exosomes that have the metalloprotease ADAM10 on their surfaces. The alpha-toxin released by S. aureus binds to these exosomes and becomes oligomerized and inactivated, providing a mechanism of innate immunity that effectively diminishes the virulence of pathogenic bacteria (i.e., MRSA).