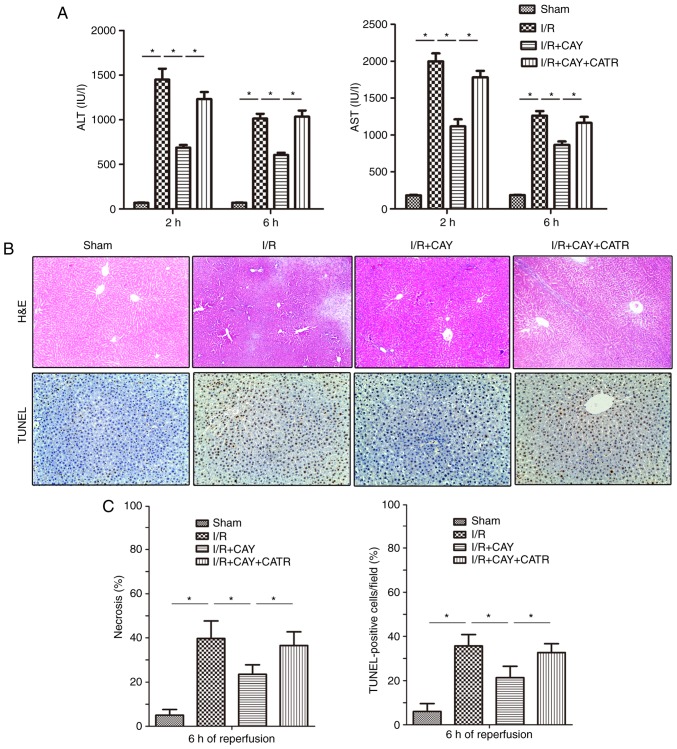
Figure 3.
EP4 agonism significantly reduces liver injury during I/R. CAY (1 mg/kg) was used to further investigate the protective effect of an EP4 agonist on hepatic I/R. (A) Serum ALT and AST levels in animals after 2 and 6 h of reperfusion. (B) H&E staining and TUNEL staining of liver tissue collected after 6 h of reperfusion; 100× magnification. In the sham group, the morphology of the liver was regular, and intact hepatocytes were observed. In contrast, large numbers of necrotic hepatocytes and disordered hepatic sinusoidal morphology were visible in the I/R groups. Only local hepatocyte necrosis was found in the I/R+CAY treatment group. (C) Percentages of necrotic cells measured in H&E-stained sections and percentages of apoptotic cells measured in TUNEL-stained sections. n=6. *P<0.05. I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; EP4, prostaglandin E receptor subtype 4; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling; CAY, CAY10598; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CATR, carboxyatractyloside.