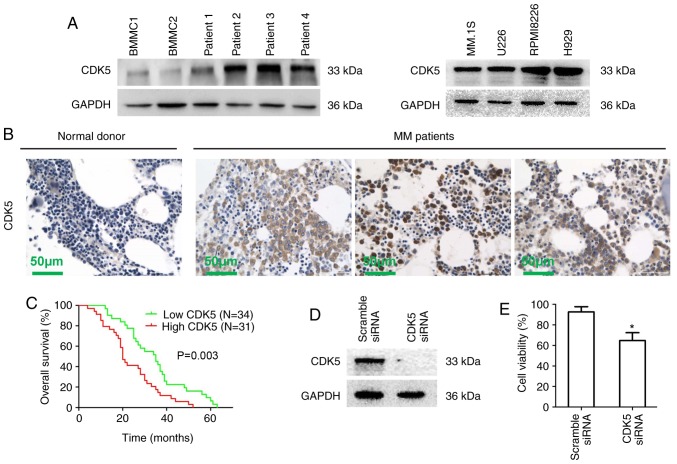
Figure 1.
Characterization of CDK5 in MM. (A) BMMCs from healthy donors, MM cells from MM patients and MM cell lines were lysed in protein lysis buffer. Protein lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with a CDK5 primary antibody. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Blots shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. (B) CDK5 expression in bone marrow biopsies from normal donors and MM patients was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Scale bar, 50 µM. (C) Kaplan-Meier overall survival curves for MM patients stratified by low (n=34) and high (n=31) expression of CDK5 (P=0.003). (D) RPMI8226 cells were transfected with scramble siRNA, CDK5 siRNA by using the cell line Nucleofector kit V. The cells were harvested 48 h posttransfection and subjected to immunoblotting with CDK5 antibody. (E) RPMI8226 cells were transfected with scramble siRNA, CDK5 siRNA followed by viability analysis using MTT assay. The percentage of cell viability was normalized to scramble siRNA control. *P<0.05 vs. control group. CDK, cyclin dependent kinase; si, small interfering; MM, multiple myeloma; BMMCs, bone marrow mononuclear cells.