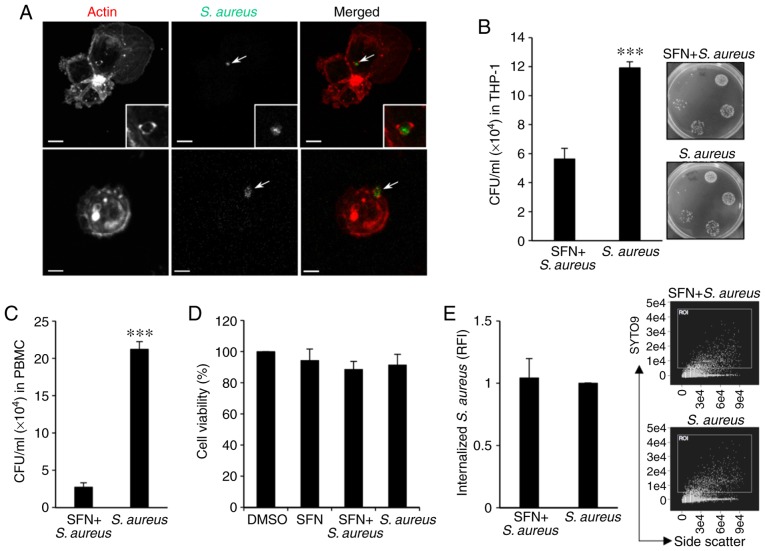
Figure 1.
SFN decreases S. aureus survival in THP-1-derived macrophages. (A) Confocal images of THP-1-derived macrophages 1 h after SYTO9-labeled S. aureus challenge. Arrows indicate S. aureus labeled with SYTO9. Actin filaments of THP-1-derived macrophages were labeled with phalloidin-ATTO 594. Scale bar, 10 µm. (B) Intracellular survival of S. aureus was determined 24 h after infection. THP-1-derived macrophages were pretreated with 10 µM SFN or DMSO for 3 h and then infected with S. aureus for 1 h prior to the addition of gentamycin to the culture medium. Intracellular S. aureus survival was evaluated by means of CFU counts. The images are tryptic soy agar plates representative of n=6 independent experiments. (C) CFU counts of S. aureus in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived macrophages with similar treatment (n=4 independent donors). (D) THP-1-derived macrophage viability was assessed after 24 h DMSO or 10 µM SFN treatment with or without S. aureus infection (1 h infection with S. aureus prior to gentamycin addition to the culture medium) by MTT assay (n=3 independent experiments). (E) Internalization of S. aureus was determined 1 h after infection of THP-1-derived macrophages with SYTO9-labeled S. aureus and analyzed by flow cytometry. The dot plots of internalized SYTO9-labeled S. aureus/side scatter are representative of n=7 independent experiments including 100,000 events each. ***P<0.001 vs. SFN + S. aureus using two-tailed unpaired t-test. SFN, sulforaphane; S. aureus, Staphylococcus aureus; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; CFU, colony forming units; RFI, relative fluorescence intensity.