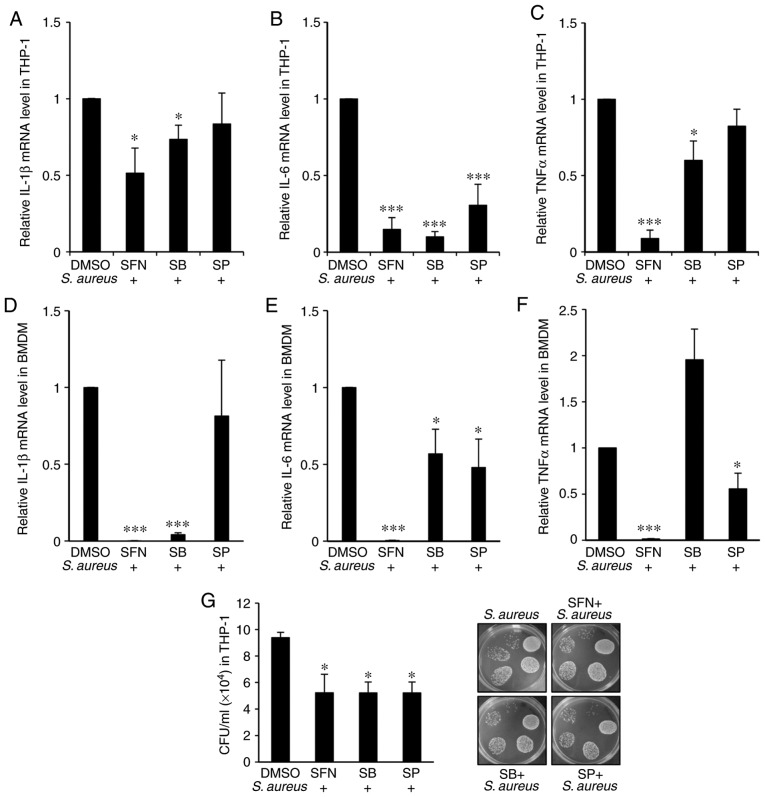
Figure 6.
SFN inhibitory effect on p38 and JNK impacts on S. aureus-mediated expression of proinflammatory genes and S. aureus survival in macrophages. (A-C) THP-1-derived macrophages were pretreated with p38 inhibitor SB or JNK inhibitor SP for 1 h prior to 10 µM SFN or DMSO treatment. After additional 3 h incubation, cells were infected with S. aureus. Total RNA was extracted 3 h post-infection and (A) human IL-1β, (B) IL-6 and (C) TNF-α mRNA expression levels were determined by RT-qPCR (n=4). (D-F) Nrf2+/− BMDMs were pretreated with SB203580 and SP600125 prior to 10 µM SFN or DMSO treatment and S. aureus infection. (D) Mouse IL-1β, (E) IL-6 and (F) TNF-α mRNA expression levels were quantified by RT-qPCR (n=5 mice). (G) Intracellular survival of S. aureus was assessed in THP-1-derived macrophages pretreated with SB and SP prior to 10 µM SFN or DMSO treatment and S. aureus infection. CFU counts were determined 24 h after infection (n=4). *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001 vs. DMSO treatment according to one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hot test. SFN, sulforaphane; p38, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; SB, SB203580; SP, SP600125; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; S. aureus, Staphylococcus aureus; IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; CFU, colony forming units.