TABLE 1.
Descriptive characteristics between adequate and inadequate plasma vitamin C categories for gender groups1
| Variable | Adequate plasma vitamin C (≥28 µmol/L) | Inadequate plasma vitamin C (<28 µmol/L) | P (2 × 2 factorial ANOVA) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | P (M vs. F adequate) | Males | Females | P (M vs. F inadequate) | ||||||
| n | Values | n | Mean ± SE | n | Mean ± SE | n | Mean ± SE | ||||
| Age, y | 20 | 65 ± 3 | 47 | 57 ± 2 | 0.08 | 7 | 73 ± 6 | 6 | 63 ± 22 | NS | 0.25 |
| Gender, % | 20 | 30 | 47 | 70 |
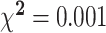
|
7 | 53.8 | 6 | 46.2 | NS |
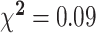
|
| BMI, kg/m2 | 20 | 27 ± 1 | 47 | 25 ± 0.4 | 0.024 | 7 | 27 ± 1 | 6 | 25 ± 1 | NS | NS |
| Smoker, % | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | NS | 2 | 28.6 | 1 | 16.7 | NS |
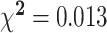
|
| Prescribed medications | 20 | 2 ± 1 | 47 | 1 ± 0.2 | 0.08 | 7 | 2 ± 1 | 6 | 1 ± 0.2 | NS | NS |
| Education, y | 20 | 13 ± 0.3 | 47 | 13 ± 0.2 | NS | 7 | 13 ± 1 | 6 | 13 ± 1 | NS | NS |
| Exercise, min/wk | |||||||||||
| Moderate intensity | 8 | 146 ± 40 | 25 | 138 ± 23 | NS | 2 | 145 ± 81 | 2 | 120 ± 81 | NS | NS |
| Vigorous intensity | 4 | 143 ± 35 | 8 | 250 ± 25 | 0.03 | 1 | 90 ± 71 | 1 | 180 ± 71 | NA | NS |
| Nutrient intake | |||||||||||
| Dose of vitamin C supplementation, mg/d | 7 | 800 ± 233 | 13 | 892 ± 168 | NS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Vitamin C dietary intake, mg/d | 20 | 86 ± 5 | 47 | 85 ± 3 | NS | 7 | 76 ± 8 | 6 | 72 ± 8 | NS | NS |
| Plasma vitamin C, μmol/L | 20 | 54 ± 4 | 47 | 53 ± 3 | NS | 7 | 18 ± 7 | 6 | 15 ± 8 | NS | NS |
| Vitamin B-12 supplementation, µg/d | 4 | 210 ± 124 | 17 | 211 ± 60 | NS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Vitamin B-12 dietary, µg/d | 20 | 3 ± 0.2 | 47 | 3 ± 0.1 | NS | 7 | 3 ± 0.4 | 5 | 3 ± 0.4 | NS | NS |
| Serum vitamin B-12, pmol/L | 20 | 439 ± 71 | 47 | 648 ± 119 | 0.02 | 7 | 269 ± 129 | 6 | 429 ± 60 | 0.07 | NS |
| Vitamin D supplementation, IU/d | 6 | 1417 ± 188 | 18 | 1556 ± 108 | NS | 1 | 1000 ± 460 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Vitamin D dietary, μg/d | 10 | 4 ± 1 | 28 | 3 ± 0.3 | NS | 4 | 3 ± 1 | 5 | 4 ± 1 | NS | NS |
| Magnesium supplementation, mg/d | 7 | 621 ± 74 | 13 | 685 ± 54 | NS | 1 | 500 ± 194 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Magnesium dietary, mg/d | 10 | 485 ± 68 | 28 | 517 ± 40 | NS | 4 | 593 ± 107 | 5 | 452 ± 96 | NS | NS |
| Fish oil/krill oil supplementation, mg/d | 4 | 1250 ± 144 | 8 | 1313 ± 92 | NS | 3 | 1167 ± 167 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Dietary omega-3, mg/d | 10 | 386 ± 94 | 28 | 594 ± 56 | 0.07 | 4 | 466 ± 149 | 5 | 101 ± 133 | NS | NS |
| Vitamin E, mg/d | 10 | 16 ± 3 | 28 | 14 ± 1 | NS | 4 | 12 ± 4 | 5 | 13 ± 2 | NS | NS |
| Vitamin B-1, mg/d | 10 | 2 ± 0.3 | 28 | 2 ± 0.2 | NS | 4 | 2 ± 1 | 5 | 2 ± 0.3 | NS | NS |
| Vitamin B-2, mg/d | 10 | 2 ± 0.3 | 28 | 2 ± 0.2 | NS | 4 | 2 ± 1 | 5 | 2 ± 1 | NS | NS |
| Vitamin B-3, mg/d | 10 | 23 ± 3 | 28 | 23 ± 2 | NS | 4 | 28 ± 5 | 5 | 25 ± 4 | NS | NS |
| Vitamin B-5, mg/d | 10 | 4 ± 0.4 | 28 | 3 ± 0.2 | NS | 4 | 3 ± 1 | 5 | 4 ± 1 | NS | NS |
| Vitamin B-6, mg/d | 10 | 1 ± 0.2 | 28 | 1 ± 0.1 | NS | 4 | 1 ± 0.3 | 5 | 1 ± 0.3 | NS | NS |
| Vitamin B-7, mg/d | 10 | 36 ± 5 | 28 | 33 ± 3 | NS | 4 | 32 ± 7 | 5 | 40 ± 6 | NS | NS |
| Iron, mg/d | 10 | 12 ± 2 | 28 | 12 ± 1 | NS | 4 | 13 ± 2 | 5 | 13 ± 2 | NS | NS |
| Zinc, mg/d | 10 | 11 ± 1 | 28 | 10 ± 1 | NS | 4 | 8 ± 2 | 5 | 12 ± 2 | 0.06 | NS |
| Iodine, µg/d | 10 | 135 ± 15 | 28 | 116 ± 9 | NS | 4 | 111 ± 24 | 5 | 125 ± 21 | NS | NS |
| Alcohol, g/d | 10 | 15 ± 3 | 28 | 3 ± 2 | <0.001 | 4 | 1 ± 4 | 5 | 1 ± 4 | NS | 0.07 |
| Caffeine, mg/d | 10 | 488 ± 114 | 28 | 557 ± 68 | NS | 4 | 742 ± 180 | 5 | 322 ± 161 | NS | 0.08 |
Values are means ± SEs unless otherwise indicated. Moderate exercise = 50–60% of maximum heart rate; vigorous exercise = 70–85% of maximum heart rate. NS: P > 0.05. NA, not applicable.
