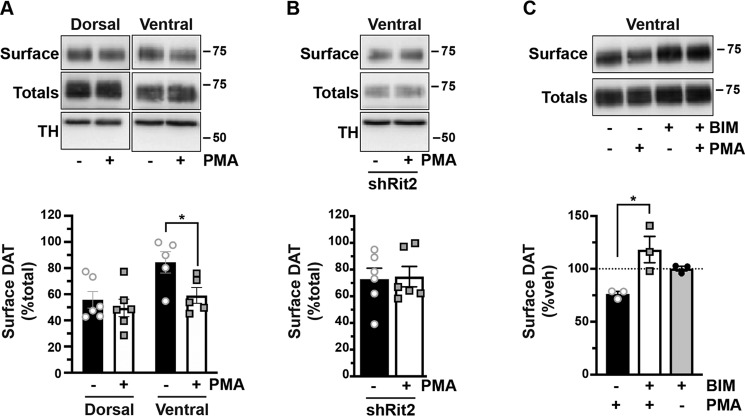
Figure 4.
PKC-induced DAT internalization in males is limited to ventral striatum and requires Rit2. Conditional Rit2 silencing in DA neurons and ex vivo striatal slice biotinylation. Male Pitx3IRES2-tTA/+ mouse VTA were bilaterally injected with either AAV9-TRE-eGFP or -shRit2. Brains were harvested 4–5 weeks postinjection, and DAT surface expression was measured in ex vivo striatal slices by surface biotinylation as described under “Experimental procedures,” following treatment with or without 1 μm PMA for 30 min at 37 °C. Representative blots are shown in the top of each panel, and average data are presented at the bottom of each panel. A, effect of PKC activation on DAT surface levels in dorsal versus ventral striatum. DAT surface levels were measured in AAV9-TRE-eGFP–injected mice and are expressed as percentage of total DAT ± S.E. (error bars) PKC activation had no effect on DAT surface expression in dorsal striatum but significantly decreased DAT surface levels in ventral striatum (two-way ANOVA: interaction: F(1, 18) = 1.96, p = 0.18; region: F(1, 18) = 7.76, p = 0.01; drug: F(1, 18) = 5.30, p = 0.03. Sidak's multiple-comparison test (vehicle versus PMA): dorsal: p = 0.76; ventral: p = 0.043, n = 5–6 slices from three independent mice. B, Rit2-KD significantly blocked PKC-stimulated DAT internalization in ventral striatum (shRit2: p = 0.86, two-tailed Student's t test, n = 6 slices from three independent mice). C, PMA-induced DAT internalization is PKC-mediated. DAT surface expression was measured in ex vivo VS slices prepared from C57Bl/6J mice and pretreated with or without 1 μm BIM I for 15 min at 37 °C prior to PMA treatment as described above. DAT surface levels are expressed as percentage of vehicle ± S.E. BIM I pretreatment significantly abolished PMA-mediated DAT surface loss (one-way ANOVA F(2, 6) = 8.08, p = 0.02; Sidak's multiple-comparison test, PMA versus BIM/PMA: *, p = 0.01, BIM/PMA versus BIM: p = 0.25, n = 3 independent mice/condition).