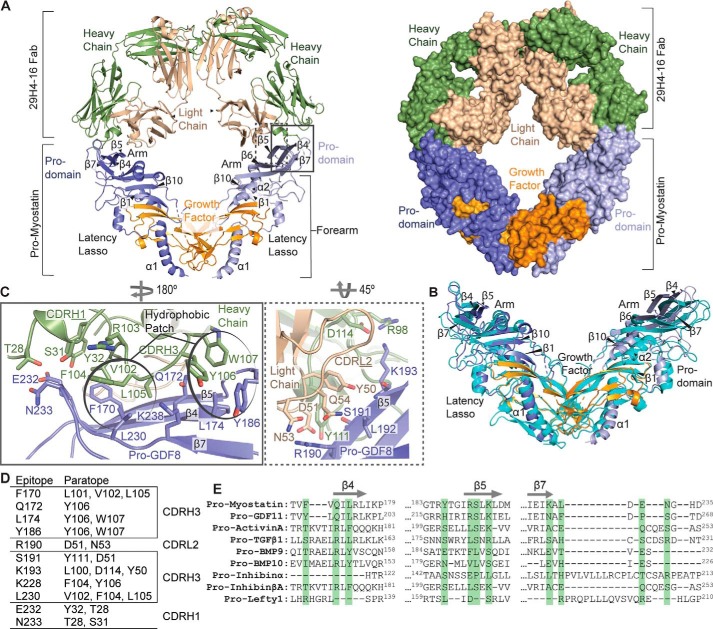
Figure 2.
Cocrystal structure of pro-myostatin–29H4-16 Fab. A, the overall structure of the pro- myostatin–29H4-16 Fab complex, showing two 29H4-16 Fabs occupying the arm regions in the prodomain of the pro-myostatin homodimer. The structure of the complex is shown in ribbon (left panel) and surface (right panel) representations. B, structural alignment of the 29H4-16 Fab–bound pro-myostatin structure (similar color scheme as in A) with the previously reported crystal structure of unbound pro-myostatin (cyan) (PDB code 5NTU). C, the binding interface of the pro-myostatin–29H4-16 complex, highlighting the key amino acid residues involved in the interaction. The left and right panels represent close-up views of the amino acid residues in the CDRs of the heavy (green) and light (light yellow) chains, respectively, that are in contact with the amino acid residues in the arm region of the pro-myostatin homodimer. The amino acid residues that cluster as hydrophobic patches in the binding interface are circled. D, summary of amino acid residues in the epitope and paratope at the binding interface of the pro-myostatin–29H4-16 Fab complex. E, sequence alignment of the regions (β4, β5, and β7) that covered the conformational epitope in pro-myostatin across related members of the TGF-β superfamily. Highlighted in green are the amino acid residues comprising the epitope in pro-myostatin.