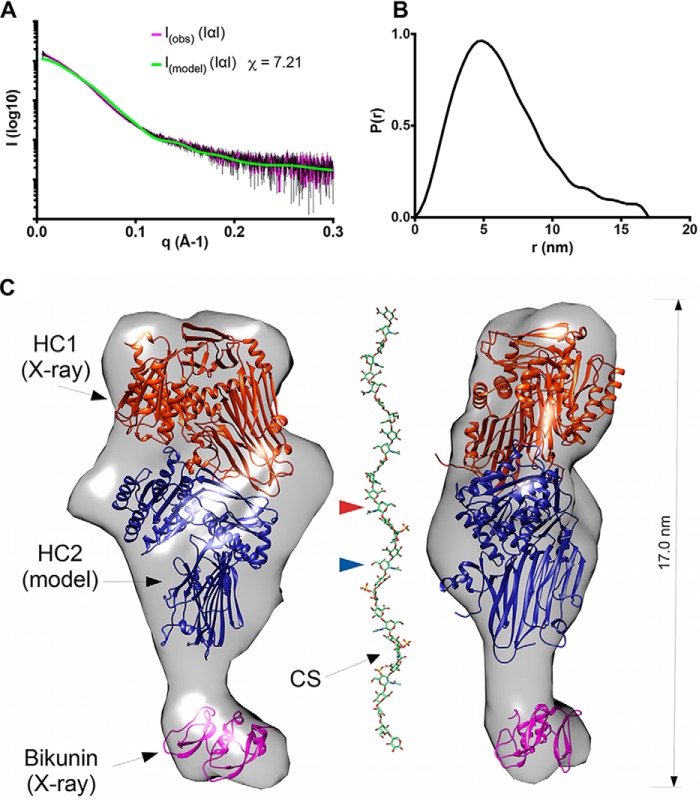
Figure 4.
The quaternary structure of inter-α-inhibitor. A, raw SAXS data for IαI (I(obs)), in the presence of 2 mm MgCl2, fitted to scattering data (pink with black error bars) derived from the pseudo atomic model (I(model)) in C calculated using Allosmod-FoXs. B, P(r) versus distance plot showing that IαI has an elongated and asymmetric shape. C, orthogonal views of the SAXS envelope of IαI (transparent gray surface) determined ab initio from the SAXS scattering curve, with structures of bikunin (PDB code 1BIK; pink) and rHC1 (determined here; orange) and a threading model of HC2 (based upon the structure of HC1; blue), modeled in. The CS chain is shown to indicate its dimensions relative to the SAXS envelope for IαI. Here the CS chain, with a standard tetrasaccharide linker, has been modeled on the sequences determined for bikunin·CS (18) with the GLYCAN-Web GAG Builder modeling tool (82), using the median values established in the Ly et al. study (a = 2, b = 1, c = 4, and d = 1, corresponding to a CS chain of 26 saccharides (18)). The CS chain is attached to S10 (in the mature bikunin sequence), which is not present in the crystal structure (PDB code 1BIK) that corresponds to residues 25–134 (44). The GlcNAc moieties in the CS chain to which HC1 and HC2 are covalently attached, via their unstructured C-terminal peptides (not shown), are indicated by arrowheads (orange and blue, respectively).