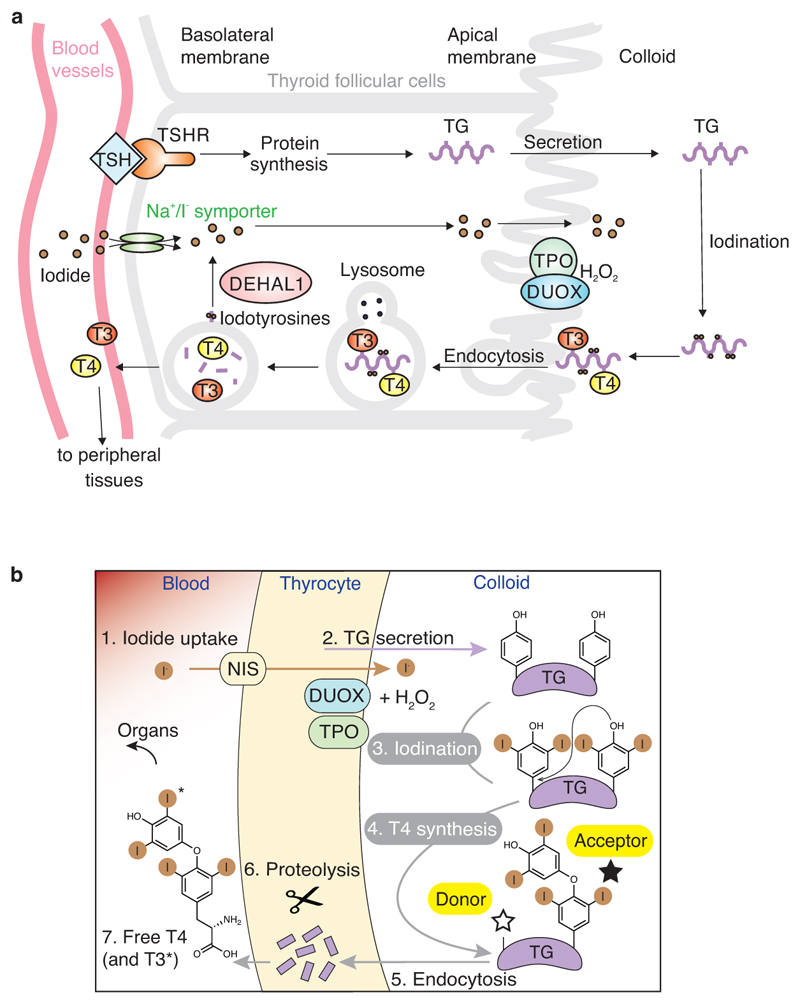
Extended Data Figure 1. The iodine cycle in the thyroid gland and the chemistry of thyroid hormone formation.
a) Iodide is extracted from the blood vessels and into the thyroid cells via the Na/I symporter (NIS). TSH binds TSH receptor (TSHR) to induce the expression of TG. TG is secreted into the extracellular lumen of follicular cells (colloid). DUOX and TPO catalyse the iodination of TG, therefore T4 (or T3) hormones are formed on the TG polypeptide chain. After hormonogenesis, TG is reimported and proteolysed in lysosomes to release T4/T3 into the blood. DEHAL1 deiodinates iodo-tyrosines to recycle iodide in thyroid cells. b) T4 (or T3) synthesis from thyroglobulin (TG) in the thyroid gland.