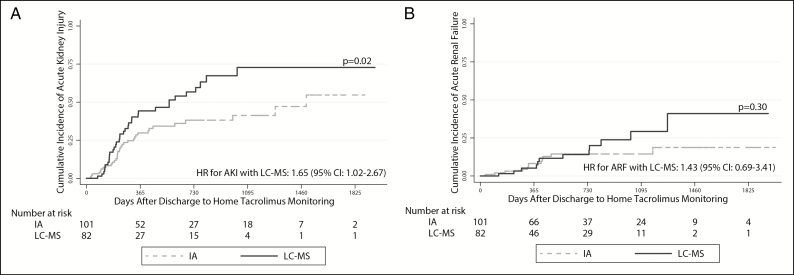
Figure 2.
Time to first acute kidney injury (AKI) (panel A) and time to first acute renal failure (ARF) (panel B) in the cohort of lung transplant recipients. The solid and dashed lines represent incidence rates in patients whose tacrolimus levels were monitored via liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and immunoassay (IA), respectively. AKI was defined as doubling of the baseline creatinine value per the RIFLE criteria. ARF was defined as a tripling of the baseline creatinine per the RIFLE criteria. Log-rank testing was used to assess for differences in cumulative incidence rates (expressed as p values). Hazard ratio (HR) values with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) represent the risk of AKI and/or ARF development in subjects monitored via LC-MS versus IA in multivariate Cox proportional hazards models adjusted for age, sex, baseline renal function, and race.