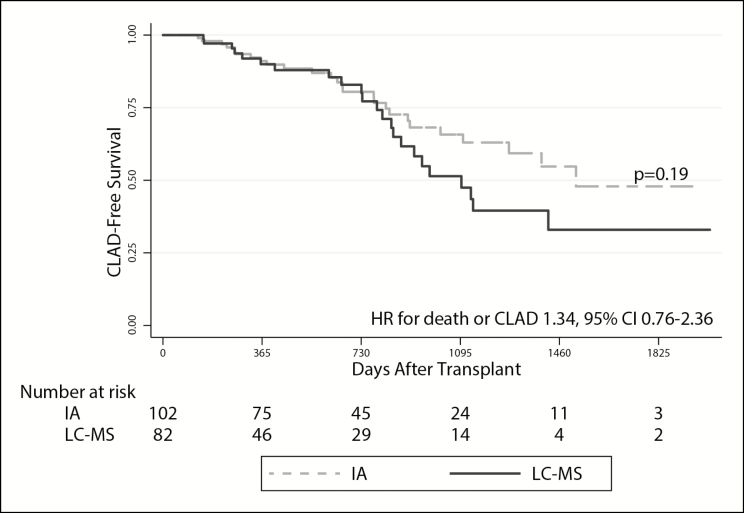
Figure 3.
Likelihood of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD)–free survival over time in the cohort of lung transplant recipients. The solid and dashed lines represent survival in patients whose tacrolimus levels were monitored via liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and immunoassay (IA), respectively. CLAD was defined as a 20% decrease from peak posttransplant forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1). Log-rank testing was used to assess for the between-group difference in CLAD-free survival (expressed as p value). The hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) represents the risk of death or development of CLAD in subjects monitored via LC-MS versus IA in multivariate cox proportional hazards models adjusted for age, sex, baseline renal function, and race.