Fig. 2.
Sensory activity is necessary for elaboration of branched endings in URX
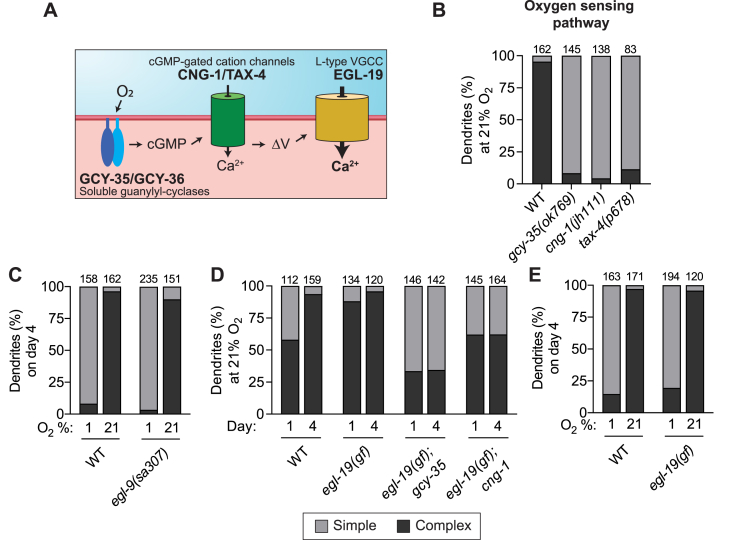
A.) Schematic showing the oxygen-sensing pathway in URX. A dendritically-localized heterodimer of GCY-35/GCY-36 produces cGMP after binding oxygen. cGMP then activates downstream CNG cation channels CNG-1 and TAX-4. Membrane depolarization subsequently gates the L-type voltage-gated calcium channel EGL-19.
B -E.) URX dendritic ending morphology was scored in worms of the given genotype and age after growth in the indicated oxygen concentration. Components of the oxygen-sensing pathway were necessary for dendritic branch elaboration, while stabilization of the hypoxia-induced transcription factor HIF-1 in the egl-9(sa307) mutant had no effect on branch growth. The gain-of-function (gf) allele egl-19(n2368) did not drive branching in worms grown at 1% oxygen, but it was sufficient to significantly increase branching in gcy-35 and cng-1 mutant backgrounds. Each bar is representative of three independently-derived transgenic strains expressing Pgcy-32::GFP to visualize URX.