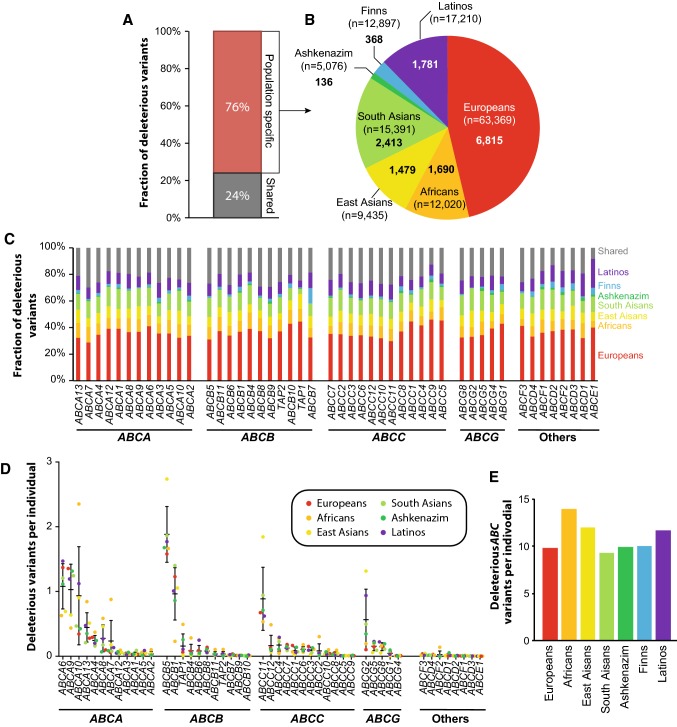
Fig. 3.
The genetically encoded functional variability of ABC transporters is highly population-specific. a The majority of genetic variations (76%) with putative functional impacts on ABC transporter function are population-specific. b Most of these population-specific variations were identified in Europeans. Numbers in bold indicate the total number of identified population-specific variations, while numbers in brackets denote the number of sequenced individuals for the respective population. c Stacked column plot showing the fraction of putatively functional variants specific to Europeans (red), Africans (orange), East Asians (yellow), South Asians (light green), Ashkenazi Jews (dark green), Finns (blue), and Latinos (purple). The fraction of variations that are found in at least two populations are shown in grey. d The number of ABC variants with functional consequences per individual is shown across populations. e Column plot depicting the functional ABC transporter variability when all putatively deleterious ABC transporter variants are aggregated. Note that African individuals harbour most functionally relevant ABC variants per individual, whereas functional variability in South Asians was overall lowest