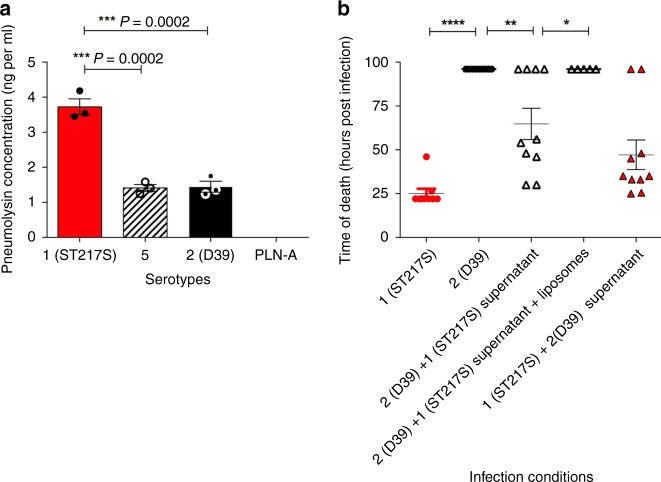
Fig. 5. High concentration of pneumolysin in infection dose correlates with high mortality rates in BALB/c mice.
a In separate tubes, 2 × 107 CFU per ml of 1 (ST217S), 2(D39), serotype 5 and PLN-A were prepared in PBS. Dose preparations were incubated at room temperature for 60 min before a sample of supernatant was removed and pneumolysin detection ELISA used to quantify the amount of pneumolysin released into the supernatant for each strain. Experiments were performed in triplicate and error bars represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison test. b Survival times of mice infected with different combinations of 106 CFU of either serotype 1 (ST217S) or serotype 2 (D39) S. pneumoniae in 50 μl bacterial dose supernatant that had been incubated at room temperature for 60 min, 10 mice per group. For one group of mice, the supernatant from ST217S was treated with liposomes (a combination of 2 μg/ml Cholesterol:sphingomyelin (66 mol/%cholesterol) and sphingomyelin-only liposomes) for 30 min. Each symbol represents one mouse. Errors bars represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test: *P-value = 0.0398, **P-value < 0.0093 and ****P-value < 0.0001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.