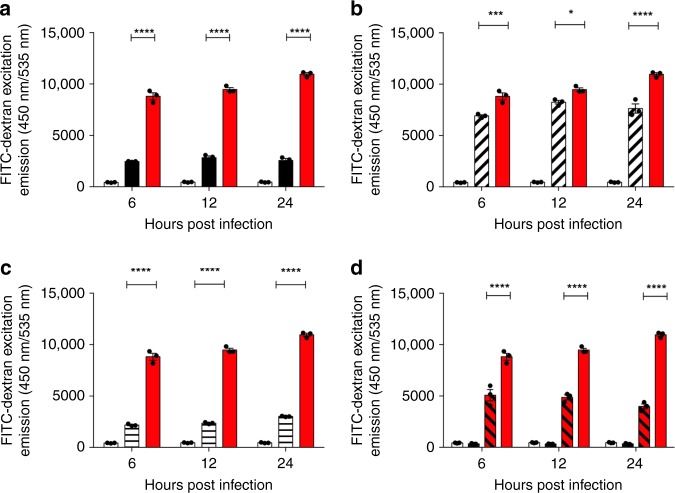
Fig. 8. African Serotype 1 causes significant increases to human primary alveolar epithelial cell barrier permeability.
Assessment of epithelial cell barrier permeability changes during infection with different S. pneumoniae serotypes was performed using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran (70 kDa, 1 mg per ml), see methods for full details. White bars represent FITC-Dextran emissions from untreated cells. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using Two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test. a Comparison of FITC-Dextran excitation emission between serotype 2(D39) (black bars) and 1 (ST217S) (red bars). ****P-value < 0.0001. b Comparison of FITC-Dextran excitation emission between serotype 5 (diagonally hashed bars) and 1 (ST217S) (red bars). *P-value = 0.0178, ***P-value = 0.0007, ****P-value < 0.0001. c Comparison of FITC-Dextran excitation emission between serotype 1 (ST306) (horizontal bars) and 1 (ST217S) (red bars). ****P-value < 0.0001. d Comparison of FITC-Dextran excitation emission between serotype 1 (ST217S) infection with (red, diagonally hashed bars) and without (red bars) the addition of liposomes. ****P-value < 0.0001. As a control, cells were also treated with liposomes in the absence of bacteria (black bars, second column). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.