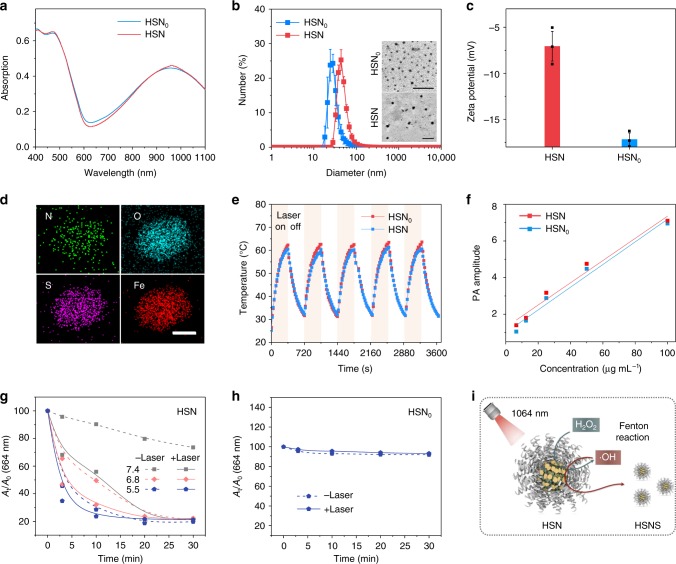
Fig. 2. In vitro characterization of HSN.
a Absorption spectra of HSN and HSN0 in 1 × PBS ([pTBCB] = 3 µg mL−1). b DLS profiles of HSN and HSN0 in 1 × PBS. Inset: TEM images of HSN0 and HSN. Scale bar: 200 nm. c Zeta potential profiles of HSN and HSN0. d STEM-EDX element mapping of HSN. Scale bar: 20 nm. e Photothermal heating-cooling cycles of HSN and HSN0 ([pTBCB] = 12 µg mL−1) under 1064 nm photoirradiation (1 W cm−2). f Linear fits of PA amplitudes of HSN (R2 = 0.96809) and HSN0 (R2 = 0.97314) as a function of concentration at 1064 nm, respectively. g ·OH generation of HSN under different pH conditions (pH = 7.4, 6.8, 5.5) with or without 1064 nm photoirradiation (1 W cm−2). ·OH generation was quantified by the decrease of absorbance of MB at 664 nm. [pTBCB] = 23 µg mL−1, [H2O2] = 0.5 mM, [MB] = 1 mM. h ·OH generation by HSN0 at pH 6.8 with or without 1064 nm photoirradiation (1 W cm−2). i Scheme of NIR-II photoirradiation enhanced self-degradation of HSN to HSNS in the presence of H2O2. Error bars indicated standard deviations of three independent measurements.