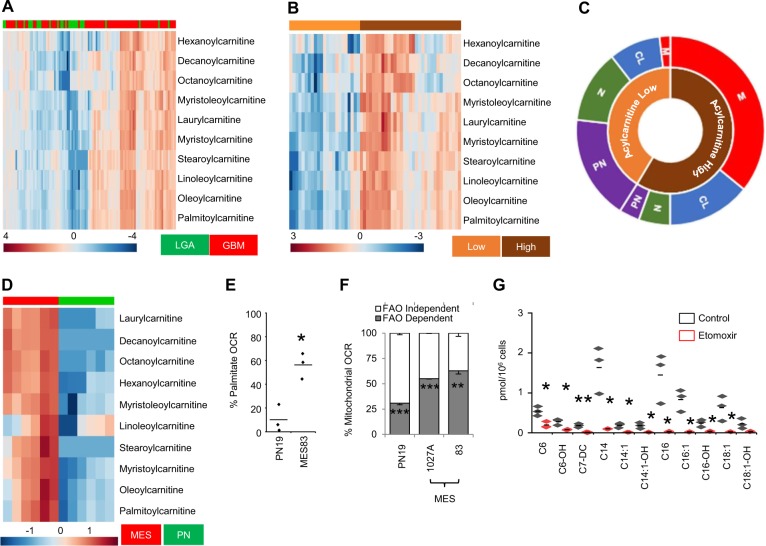
Fig. 1. FAO related metabolites differentially accumulate in GBM.
a Unsupervised clustering of patient-derived low-grade astrocytoma (LGA; n = 28) and glioblastoma (GBM; n = 80) demonstrates an accumulation of medium and long-chain acylcarnitines in GBM. b Heterogeneous clustering of acylcarnitines is observed in GBM (n = 56), demonstrating acylcarnitine “high” and “low” metabolic phenotypes. c The acylcarnitine “high” phenotype is enriched with mesenchymal (M) and classical (CL) subtypes, while neural (N) and proneural (PN) subtypes are enriched in the acylcarnitine “low” phenotype. d Unsupervised clustering of two patient-derived mesenchymal (MES) and two proneural (PN) GBM stem cell lines demonstrate an accumulation of medium and long-chain acylcarnitines (n = 3). e Cellular oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured in real time in PN and MES cells using the Seahorse platform (n = 3). Results represent percent increases in OCR following the addition of palmitate (300 µM). f Basal mitochondrial OCR was measured in stated cell lines treated with +/− etomoxir (40 µM; 45 min; n = 3). g Medium and long chain acylcarnitines were quantified in MES83 cells treated with +/− etomoxir (40 µM; 24 h; n = 3). Data represents mean ± SD (F) and line between the data points represents mean. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0005.