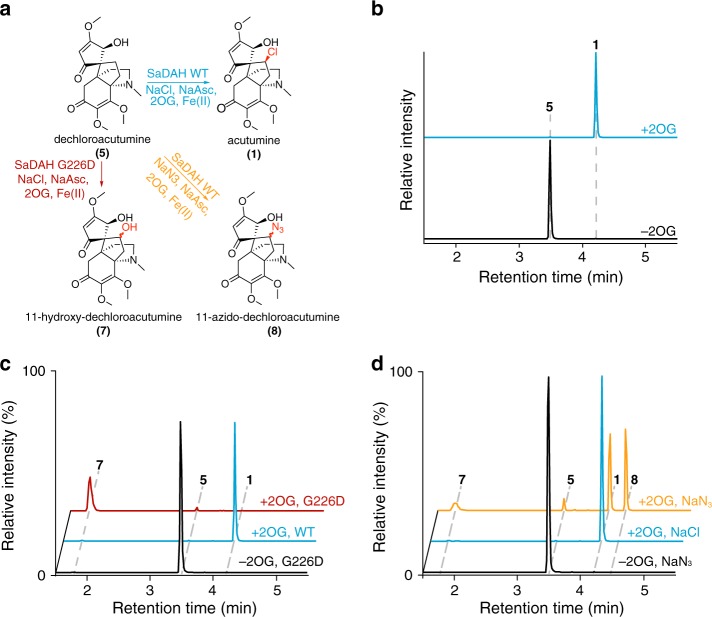
Fig. 2. Functional characterization of DAH and its G226D mutant by in vitro enzyme assays.
a Alternative catalytic activities of SaDAH-WT and SaDAH-G226D. The chlorination, hydroxylation and azidation activities are colored in blue, red, and yellow, respectively. The putative regiochemistry of the −OH and −N3 in 7 and 8 are highlighted in red, while the stereochemistry of the products remains undetermined. b XICs showing the in vitro activity of SaDAH-WT that chlorinates 5 to yield 1 in a 2OG-dependent manner. c XICs showing the in vitro activity of SaDAH-G226D that predominantly hydroxylates 5–7 in a 2OG-dependent manner. The chlorination product 1 is also produced as a minor product. d XICs showing the 2OG-dependent azidation activity of SaDAH-WT that converts 5–8 in reaction buffer containing 1 mM NaN3. The chlorination product 1 and the hydroxylation product 7 are also produced as side products. Mass windows used for displaying the XICs: 5, 364.176 m/z; 1, 398.137 m/z; 7, 380.17 m/z; and 8, 405.18 m/z.