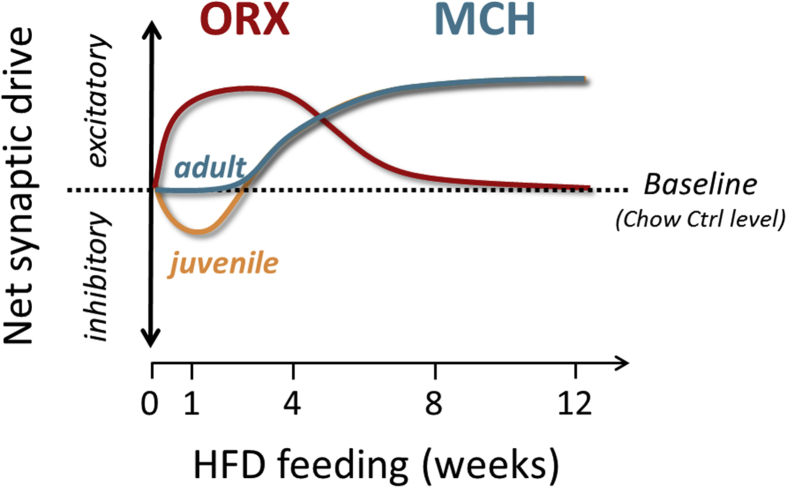
Figure 8.
Net change in synaptic properties of ORX and MCH neurons over the course of HFD feeding. A schematic summarizing the time course of synaptic changes in ORX and MCH neurons due to HFD. In ORX neurons, excitatory synaptic transmission increases during the acute phase (from 1 day to 4 weeks). All of the excitatory changes return to chow Ctrl levels (baseline) by week 11 of HFD. In contrast, HFD does not influence inhibitory synaptic transmission. Thus, the net change in synaptic drive or the balance between excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs to ORX neurons is excitatory in the early phase of HFD, which normalizes with prolonged feeding. In MCH neurons, excitatory synaptic transmission decreases after the first week of HFD. Note that this inhibitory effect is specific to adolescence and is not seen in adulthood. As the HFD exposure persists, the excitatory synaptic drive starts to increase by week 4 and continues to increase with prolonged feeding. In contrast, HFD has no effect on inhibitory synaptic transmission to MCH neurons. Thus, the net synaptic drive follows the changes in excitatory transmission.