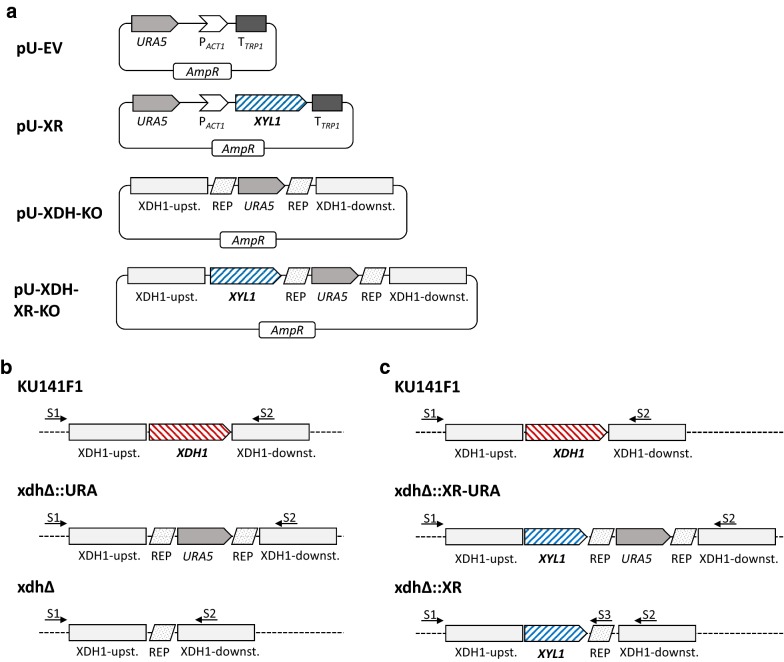
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of the plasmids used and generated in this study, and the resulting genetic modifications. a shows the vectors used in this study: pU-EV is the empty vector used as control, pU-XR is used for the overexpression of the xylose reductase gene XYL1, pU-XDH-KO for the knockout of the xylitol dehydrogenase gene XDH1, and pU-XDH-XR-KO for genomic replacement of XDH1 by XYL1. b Deletion of XDH1 by homologous recombination of the selection cassette (xdh∆::URA) and after release of URA5 by Ura-Blaster (xdhΔ) in the parental strain M. guilliermondii KU141F1. c Replacement of XDH1 by XYL1 (xdh∆::XR-URA) and after release of URA5 by Ura-Blaster (xdh∆::XR) in the parental strain KU141F1; AmpR: Ampicillin resistance gene; URA5: selection marker for uridine-prototrophy, PACT1: ACT1 promotor for constitutive expression of XYL1, TTRP1: Terminator of XYL1 expression; REP: repetitive sequences for the use of the Ura-Blaster system to release URA5 selection marker; XDH1-upstr.: genomic sequence 1000 bp upstream of XDH1; XDH1-downst.: genomic sequence 1000 bp downstream of XDH1; S1, S2 and S3 indicate sequencing primer binding sites