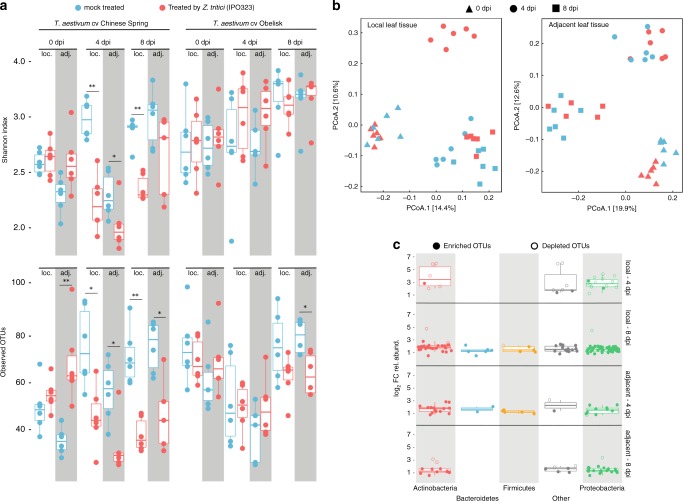
Fig. 5. Infection by Z. tritici alters the wheat microbiota in local and adjacent leaf tissues.
a Two measures of the community composition, Shannon index and observed OTUs, are depicted in upper and lower panels, respectively. Reads were rarefied to an even sequencing depth corresponding to the smallest simple size of 601 reads. Community composition in leaf samples treated by Z. tritici (red boxplots) were compared to mock treatment (blue boxplots) for each corresponding time point (i.e., 0, 4, and 8 dpi-f) and leaf tissue types, local (loc.) and adjacent (adj.). Infection by Z. tritici leads to a significant drop in the computed Shannon indexes and observed OTUs in both types of leaf tissues (local and adjacent). Testing for significance was performed using a Kruskal–Wallis rank sum test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. b Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) computed on Bray-Curtis distances of microbial communities associated with T. aestivum cultivar Chinese Spring. Each shape in the plot represents the community structure of one sample. Red- and blue-colored shapes designate mock- and Z. tritici-treated leaf samples as in (a). PCoA plots in the left and right panels correspond to local (left) and adjacent (right) leaf tissues, respectively. c Boxplot depicting log2 fold changes in the relative abundance of OTUs. Colors in the graph depict bacterial phyla. OTUs with P > 0.05 were filtered out. Filled and unfilled circles indicate OTUs that are significantly enriched and depleted, respectively, from Z. tritici-treated leaf samples compared to mock-treated samples. Number of biologically independent replicates: n = 6.