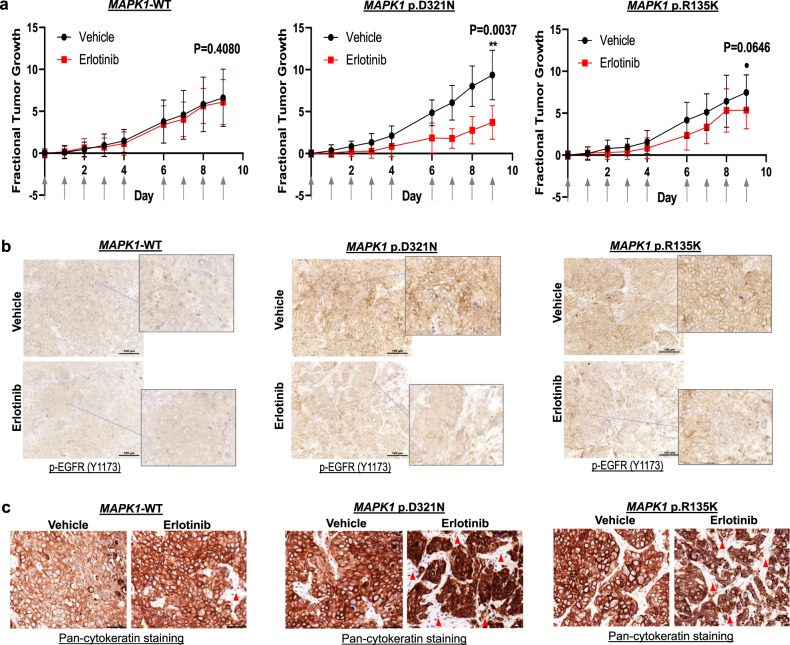
Fig. 2. MAPK1p.D321N mutation confers erlotinib sensitivity in vivo.
a Fractional tumor growth curves of in vivo tumor expressing MAPK1-WT, MAPK1p.D321N, or MAPK1p.R135K (mean tumor sizes with SEM). FaDu cells expressing MAPK1-WT, MAPK1p.D321N, and MAPK1p.R135K, respectively, were inoculated into nude mice subcutaneously (8 × 105 cells per inoculation). Mice with tumor expressing respective MAPK1-WT/mutations were randomized into erlotinib (erlotinib dissolved in 10% HP-β-CD) or vehicle (10% HP-β-CD) treatment groups (N = 8 tumors per group). Treatment started when tumors were palpable and reached the size ~3 × 3 – 4 × 4 mm2. Erlotinib or the vehicle control were administered by oral gavage (50 mg/kg erlotinib or the corresponding vehicle amount) for five consecutive days as indicated by the arrows on the X-axis. b IHC staining showing membranous p-EGFR expression of these xenografts post erlotinib/vehicle treatments (N > 3 per group). A total of 100 µm scale bars were shown. c IHC staining showing corresponding pan-cytokeratin expression in these tumors post erlotinib/vehicle treatment (N > 3 per group). A total of 50 µm scale bars were shown.