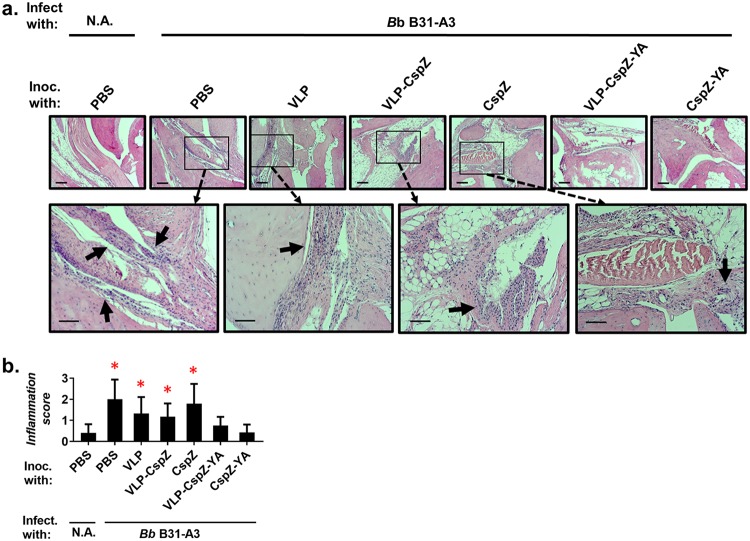
FIG 2.
Vaccination of VLP-CspZ-YA- or CspZ-YA-protected mice from LD-associated arthritis caused by tick feeding. Five PBS-inoculated C3H/HeN mice, six VLP-CspZ-, VLP-CspZ-YA-, or CspZ-YA-inoculated C3H/HeN mice, or seven VLP- or CspZ-inoculated C3H/HeN mice were fed on by nymphs carrying B. burgdorferi strain B31-A3. Uninfected nymphs were placed on an additional five mice inoculated with PBS as a negative control (N.A.). Tibiotarsus joints were collected from these mice at 21 dpf. To assess inflammation, tissues were fixed and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. (a) Representative images from one mouse per group are shown. Top panels are lower-resolution images (joint, ×10 magnification [bar, 160 μm]); bottom panels are higher-resolution images (joint, ×20 magnification [bar, 80 μm]) of selected areas (highlighted in top panels). Arrows indicate infiltration of immune cells. (b) To quantitate inflammation of joint tissues, at least 10 random sections of tibiotarsus joints from each mouse were scored on a scale of 0 to 3 for the severity of arthritis. Data shown are the mean inflammation score ± standard deviation of the arthritis scores from each group of mice. Asterisks indicate the statistical significance (P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons) of differences in inflammation relative to that of uninfected mice.