Figure 3.
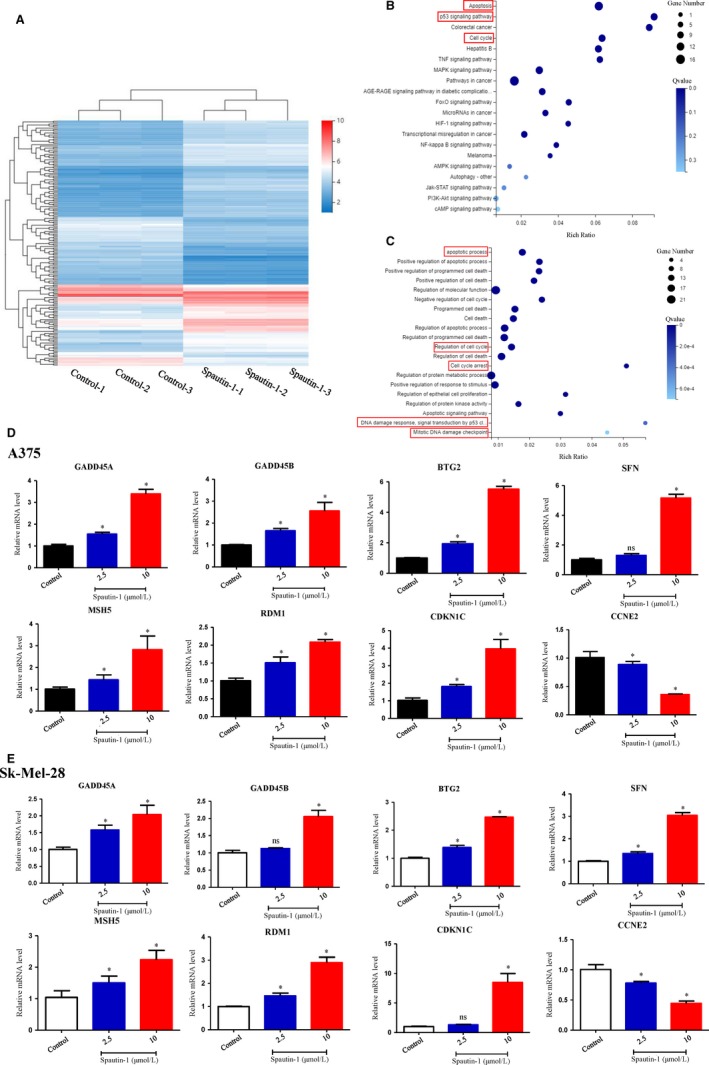
Transcriptomics coupled with qRT‐PCR identified apoptosis and DNA damage as potential mechanisms underlying spautin‐1‐mediated anti‐tumour effect. A, Sk‐Mel‐28 cells were treated with 10 µmol/L Spautin‐1 for 48 h. Cluster analysis of the genes expressed in each comparison group, displaying with a heat map. B, The pathways correlate with the differential expression genes was analysed by enriched KEGG pathway. The enriched bubble chart shows the relative top 20 enriched pathways. C, Gene Ontology analysis of the relative differential expression genes. Only top 20 enriched pathways are shown in the bubble chart. D and E, A375 (D) and Sk‐Mel‐28 (E) were treated with various dosages of spautin‐1 for 48 h. The key differential expression genes related to cell cycle and DNA damage were validated by qRT‐PCR. (Mean values ± SEM, n = 3) Significant differences were evaluated using a one‐way ANOVA. *P < .05 vs control
