Figure 1.
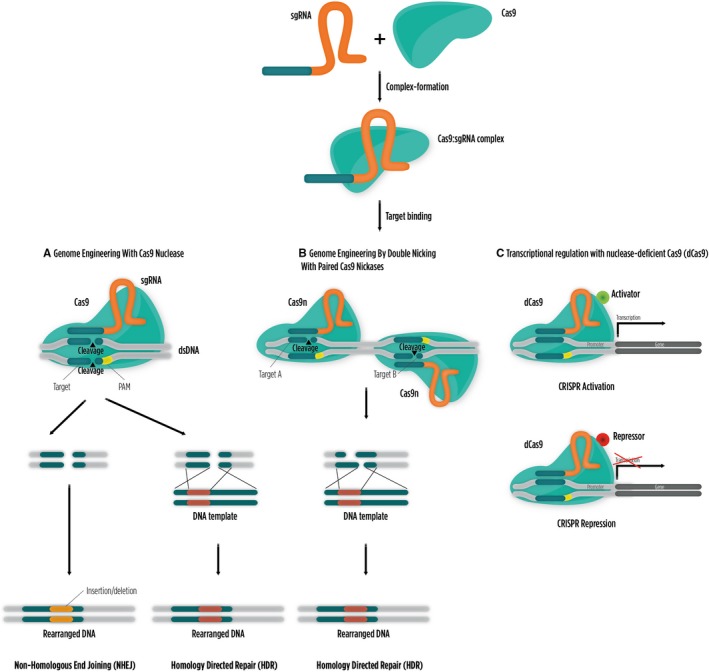
CRISPR/Cas9 genome‐editing tools in mammalian cells. (A) Double‐stranded DNA breaks (DSBs) are generated by CRISPR/Cas9 system, which triggers endogenous DNA repair mechanisms resulting in genetic manipulation. Non‐homologous end joining (NHEJ) is an error‐prone mechanism that is able to disrupt the target gene through the formation of insertions/deletions (indels). Alternatively, homology‐directed repair (HDR) could be activated in the presence of a properly designed DNA repair template to alter a DNA sequence at a specific locus. (B) Mutated Cas9 with only nickase activity (Cas9n) makes a site‐specific single‐stranded nick and does not activate NHEJ. Double‐stranded breaks only occur upon delivery of two sgRNAs that can be later repaired by HDR or NHEJ. (C) Nuclease‐deficient Cas9 (dCas9) can be fused to different effector domains, which allow for the activation or repression of particular target genes in their native context without creating DSBs
