E-Figure 1-25.
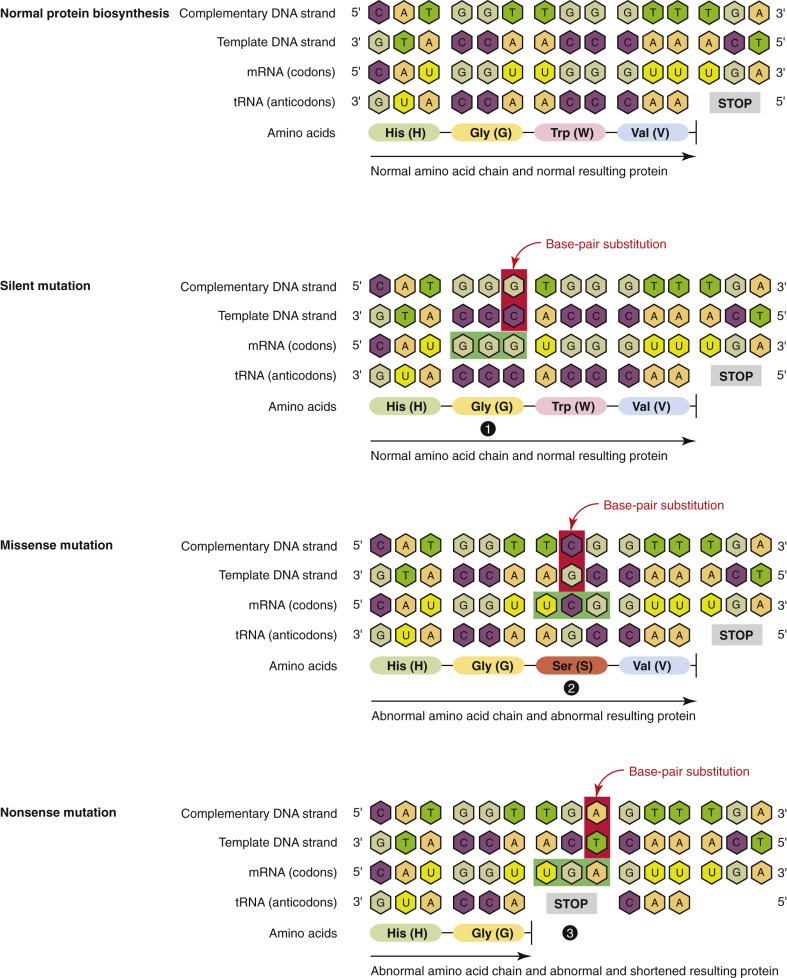
Types of Base-Pair Substitutions in Gene Mutations.
1, Silent mutations. Base-pair substitutions in silent mutations change the messenger RNA (mRNA) codons (GGU to GGG in the example); however, the mutated codons (GGG) code for the same amino acid as the original mRNA codons, so the synthesis of the polypeptide is unaffected. 2, Missense mutations. Base-pair substitutions in missense mutations change the mRNA codons (UGG to UCG in the example); the mutated codons (UCG) code for a different amino acid than the original mRNA codons, so the synthesis of the polypeptide is altered. 3, Nonsense mutations. Base-pair substitutions in nonsense mutations change the mRNA codons (UGG to UGA in the example); the mutated codons (UGA) are a “stop” code, prematurely halting polypeptide chain synthesis. tRNA, Transfer RNA.
(Courtesy Dr. M.A. Miller, College of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University; and Dr. J.F. Zachary, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Illinois.)
