FIGURE 1.
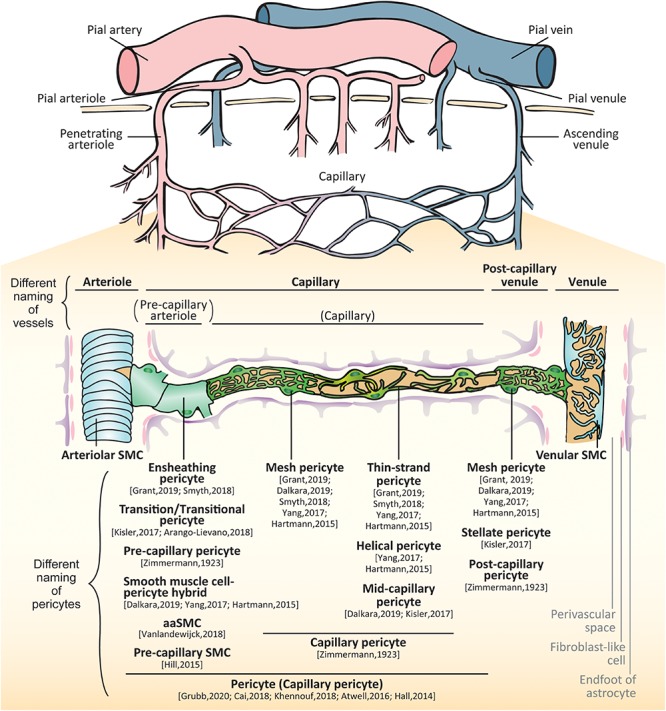
Brain vessels and mural cells. The pial arterioles branch from pial arteries which follow the outer rim of the brain via the meninges. The arterioles penetrate perpendicularly into the brain parenchyma (penetrating arteries) and further split into smaller arterioles. As their diameters and constituent cell types are changed, the vessels make a transition to capillaries. The capillary join to form venules that collect into pial venules and further into pial veins. In the small vessels, there are two types of mural cells separately located outside of endothelial layer: vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and pericytes. SMCs are localized at the arteries, arterioles, venules and veins whereas pericytes are localized at the capillaries and post-capillary venules. The proximal branches coming off penetrating arterioles are sometimes called as pre-capillary arterioles. The subtypes of pericytes are differently called: ensheathing pericytes, transitional pericytes, pre-capillary pericytes, smooth muscle cell-pericyte hybrids, arteriole SMC (aaSMCs), or pre-capillary SMCs in a few branches from arterioles; capillary pericytes, mesh pericytes, thin-strand pericytes, helical pericytes, or mid-capillary pericytes in the middle part of capillary; mesh pericytes, stellate/stellate-like pericytes, or post-capillary pericytes in the post-capillary venules.
