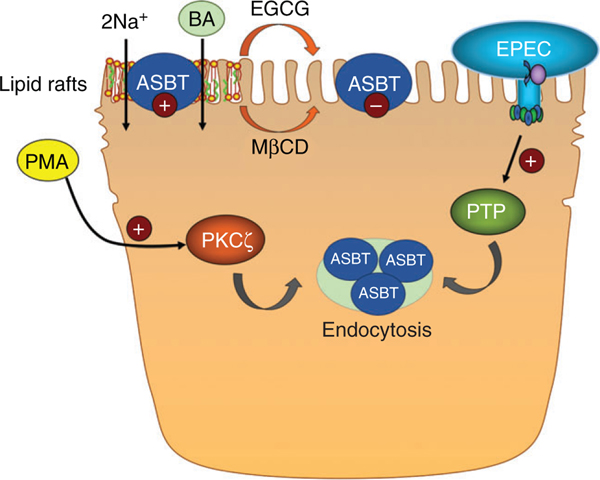
Figure 5.
Acute, posttranslational regulation of ASBT. Functional ASBT, which transports two Na+ ions along with one bile acid, is present in lipid rafts. Movement of ASBT out of rafts, either by the green tea catechin (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) or methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD), decreases ASBT function. Activation of protein kinase C ζ (PKCζ) by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) results in endocytosis and reduced function of ASBT. Similarly, activation of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTP) by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) causes endocytosis of ASBT.