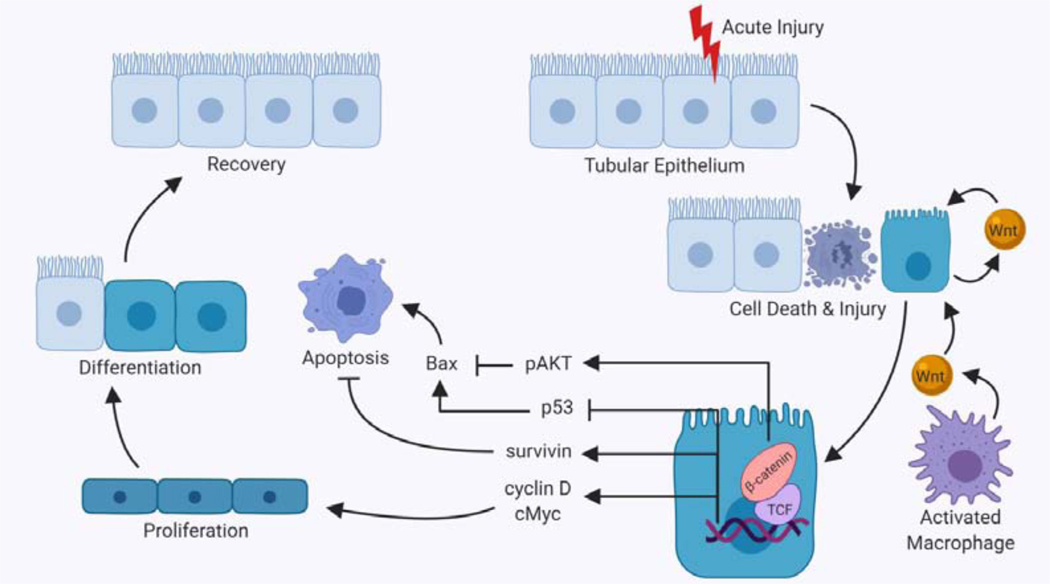
Figure 2. Effect of Wnt signaling in acute kidney injury.
Acute injury to the kidneys results in death and injury to tubular epithelial cells. These damaged cells secrete both Wnts and pro-inflammatory cytokines, resulting in recruitment of macrophages, which further contribute to Wnt pathway activation. Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in tubular epithelium has many downstream effects which primarily result in proliferation or prevention of apoptosis. Apoptosis is prevented through the inhibition of pro-apoptotic Bax, mediated by β-catenin-dependent phosphorylation of Akt and/or inhibition of p53. Wnt/ β-catenin signaling also promotes cell survival through increased expression of survivin. The target genes activated by Wnt/β-catenin signaling include cyclin D and cMyc, both of which are pro-proliferative proteins. Proliferation helps to replace cells killed during the injury and differentiation of these injured and replacement cells leads to recovery. This figure was created with Biorender.com. Abbreviations: Bax, B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) associated X protein; Akt, protein kinase B; TCF, T-cell factor.