Fig. 5. Lentivirus-mediated loss- or gain-of-miR-15a/16–1 function increases or decreases in vitro angiogenesis, respectively.
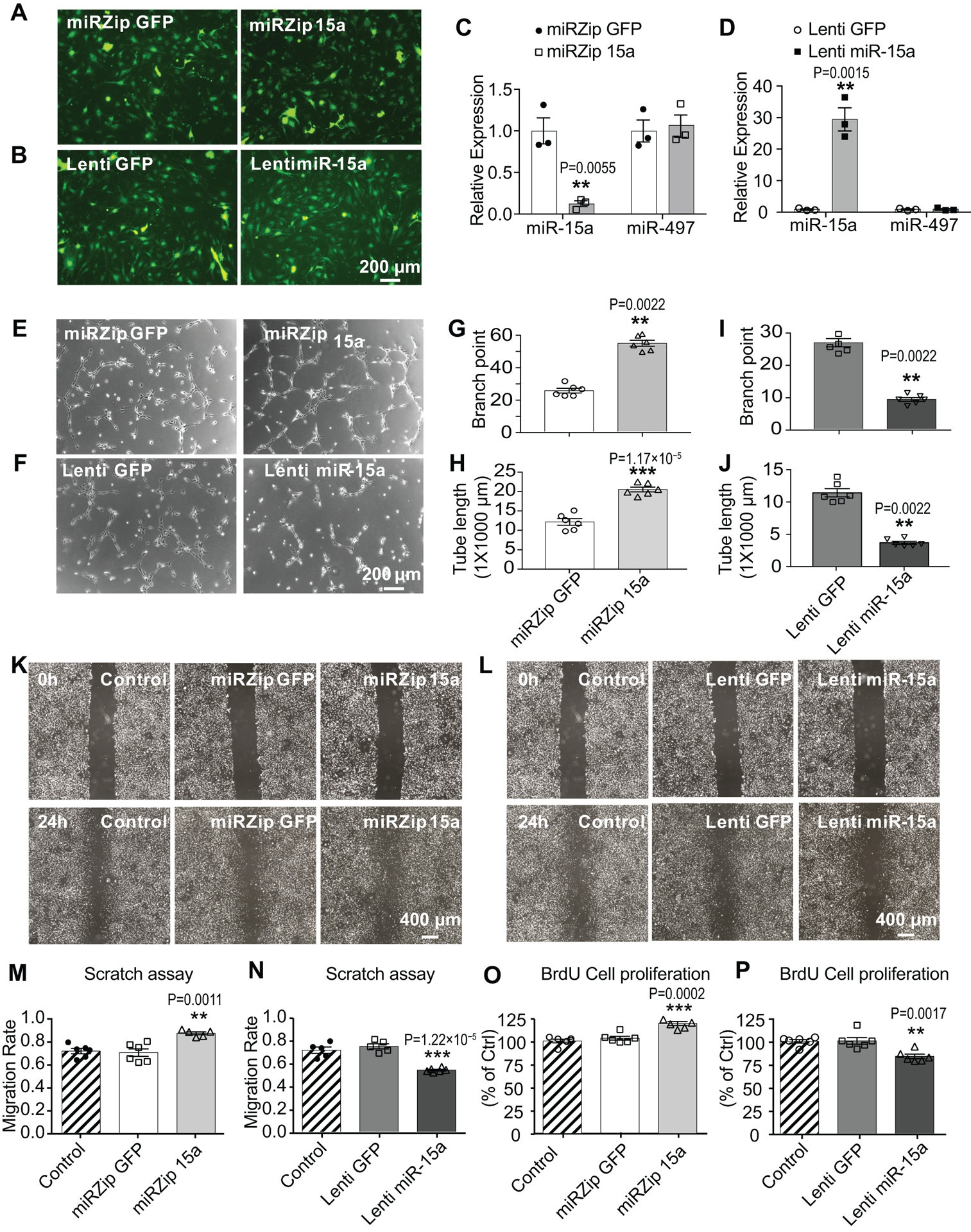
A-B, mBMECs were infected with lentivirus (1–2 MOI) containing small hairpin miR-15a (miRZip 15a, A) or pre-miR-15a (Lenti miR-15a, B) for 48–72h. C-D, qPCR data showed statistically significantly reduced miR-15a levels in mBMECs after infection with miRZip 15a (C), while elevated miR-15a levels after infection with Lenti miR-15a (D), compared to their GFP controls. No statistically significant change was detected for miR-497 expression. n = 3; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus miRZip GFP or Lenti GFP groups; statistical analyses were performed by two-tailed Student’s t-test. E-J, Capillary tube formation assay indicated that, loss-of-miR-15a function by miRZip 15a statistically significantly increased tubular-like structure (E), branch points (G) and total tube length (H). On the contrary, gain-of-miR-15a function by lentivirus dramatically reversed these effects (F,I,J). n = 6; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus miRZip GFP or Lenti GFP groups; statistical analyses were performed by Mann-Whitney test for G,I,J, and by two-tailed Student’s t-test for H. K-N, In vitro scratch assay in mBMEC cultures after lentiviral infections. Representative images (K) and quantitative analysis (M) showed that loss-of-miR-15a function by miRZip 15a statistically significantly increases the endothelial migration compared to miRZip GFP group or non-transduction control, whereas gain-of-miR-15a function (L,N) by Lenti miR-15a statistically significantly reverses this effect. n = 5–6; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus miRZip GFP or Lenti GFP groups; statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests. O-P, BrdU incorporation assays showed that, lentivirus-mediated loss-of-miR-15a function in mBMECs statistically significantly up-regulated (O) while gain-of-miR-15a function statistically significantly down-regulated (P) cell proliferation, compared to lentiviral GFP groups or non-transduction controls. n = 6; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus miRZip GFP or Lenti GFP groups; statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests.
