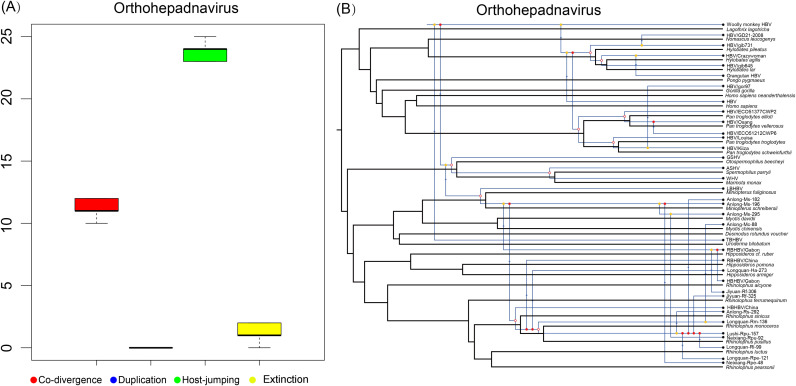
Fig. 6.
Co-phylogenetic analyses of hepadnaviruses and their associated mammal hosts. (A) Box plots indicate the relative frequency of different co-phylogenetic events. (B) One reconciliation of the hepadnavirus tree is shown in blue while the corresponding host phylogeny is shown in black. The host tree was based on mitochondrial cytochrome b (mt-cyt b) gene sequences, and the hepadnavirus tree was based on the P gene. Filled circles at the nodes indicate co-divergence events, empty circles mark lineage duplication events, arrows indicate host-switching events, and dotted lines show loss events.