Figure 1.
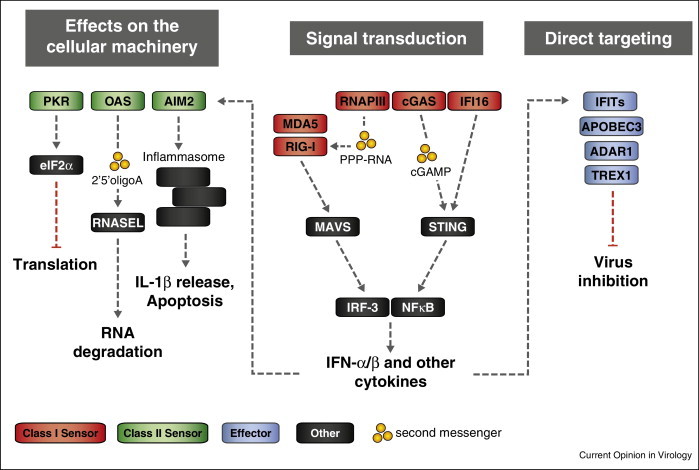
Viral nucleic acid sensor and effector proteins and their primary antiviral properties. Engagement of a particular set of nucleic acid sensors (Class I sensors, red) results in signal transduction events, leading to expression of the type I interferons IFN-α/β and other cytokines. These in turn upregulate additional sensors (Class II sensors, green) with the ability to modulate the cellular machinery. In addition cytokines induce expression of effector proteins (blue) directly targeting viral nucleic acids. Transmission of signals in some pathways occurs through second messengers (yellow). Class II sensors include PKR, OAS and AIM2. PKR phosphorylates translation initiation factor eIF2α and consequently inhibits translation. Activated OAS synthesises the second messenger 2′5′ oligoA, which then binds to and activates the latent endoribonuclease RNASEL. Activation of the inflammasome, a large multimeric complex including pro-caspase-1, is mediated by the DNA sensor AIM2. Caspase-1 cleaves its substrates pro-IL-1b and IL-18 for extracellular release. For signal transduction, MDA5 and RIG-I (either activated directly or through binding of RNAPIII-synthesised PPP-RNA) engage the adaptor protein MAVS. cGAS and IFI16 transmit their signal to the adaptor STING. Both pathways culminate in phosphorylation and dimerization of IRF-3 as well as release of active NFκB into the nucleus, where they cooperate to form an enhanceosome to turn on transcription of cytokine genes.
Abbreviations: OAS, 2′5′ oligoadenylate synthetase; PKR, dsRNA-dependent protein kinase R; AIM2, absent in melanoma 2; eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit; RNASEL, 2-5A-dependent ribonuclease L; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; RIG-I, retinoic acid inducible gene I; RNAPIII, RNA polymerase III; cGAS, cyclic GMP–AMP synthase; IFI16, interferon gamma-inducible protein 16; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; IRF-3, interferon regulatory factor 3; NFκB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells; IFIT, interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats; APOBEC3, apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3; ADAR1, RNA-specific adenosine deaminase 1; TREX1, three prime repair exonuclease 1; PPP-RNA, 5′ triphosphorylated RNA.
