Figure 2.
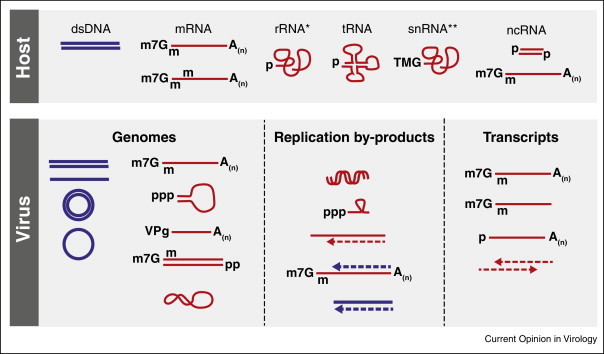
Differences between cellular and viral nucleic acids. Synthesis of host RNA (red) from nuclear dsDNA (blue) is achieved by three cellular RNA polymerases. RNA polymerase II synthesises mRNA, ncRNA and some snRNAs, whereas RNA polymerase III generates tRNA and 5S rRNA. rRNAs are produced by RNA polymerase I. Virus-derived DNA and RNA are present in the cell either as genomes, transcripts or replication by-products. Indicated are particular differences at the RNA 5′ and 3′ end, such as cap structures and methylations (e.g. cellular mRNA harbouring an N7-methylated guanine cap structure and 2′O-methylation at the first and/or second ribose). *5S rRNA harbours a 5′ triphosphate group; **U6 and 7SK RNA both have a 5′ gamma-monomethyl phosphate, and SRP RNA has a 5′ triphosphate. Abbreviations: ds, double-stranded; mRNA, messenger RNA; rRNA, ribosomal RNA; tRNA, transfer RNA; snRNA, small nuclear RNA; ncRNA, non-coding RNA; m7G, N7-methylated guanine cap; m, 2′O-methylation; p, phosphate group; TMG, hypermethylated 2,2,7-trimethylguanosine cap; VPg, viral protein genome-linked; A(n), poly(A) tail.
