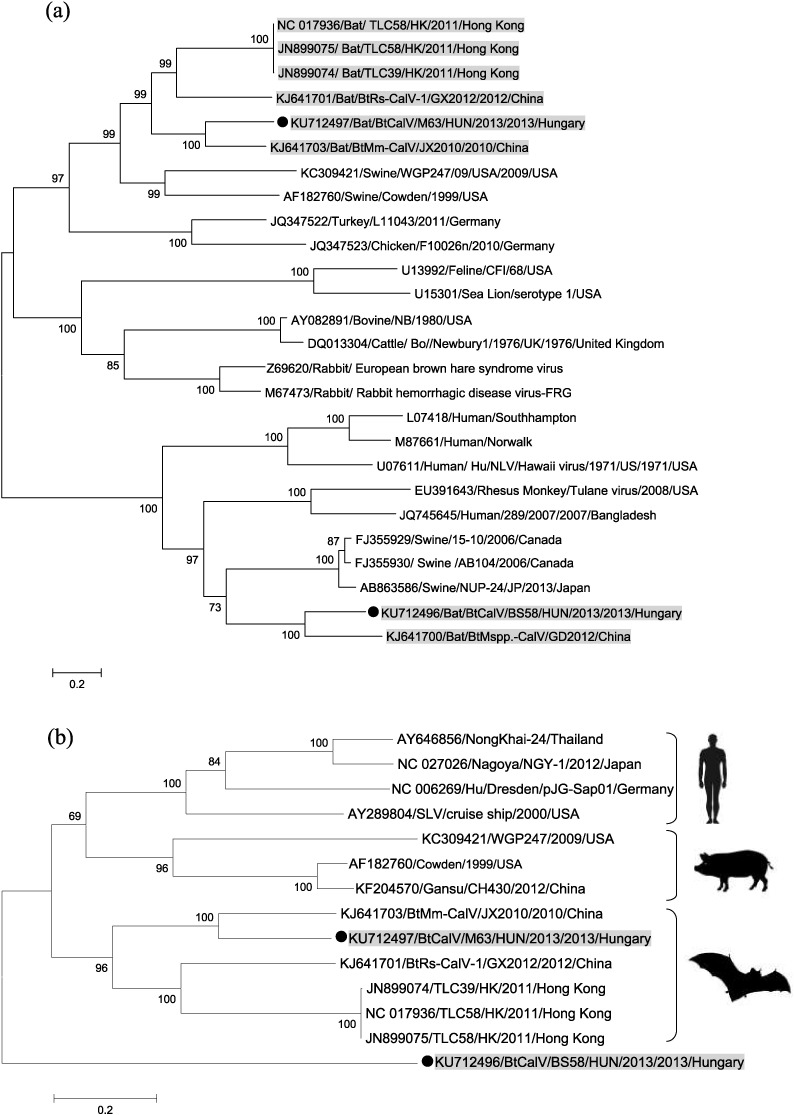
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree of the two novel bat calicivirus sequences and their relationship with other known genera within the family Caliciviridae (a) and relationship with sapoviruses (b) identified from human, swine and bats. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on a partial sequence of 3130 nucleotides, incorporating the whole capsid region of the viruses. Strains reported in this study are marked with black dots, and all bat derived calicivirus strains are marked with gray background. The phylogenetic trees were constructed with MEGA v5.0 software using the Maximum-Likelihood method, based on the General Time Reversible model with Gamma Distribution (GTR + G). Number of bootstraps for simulations was 1000.