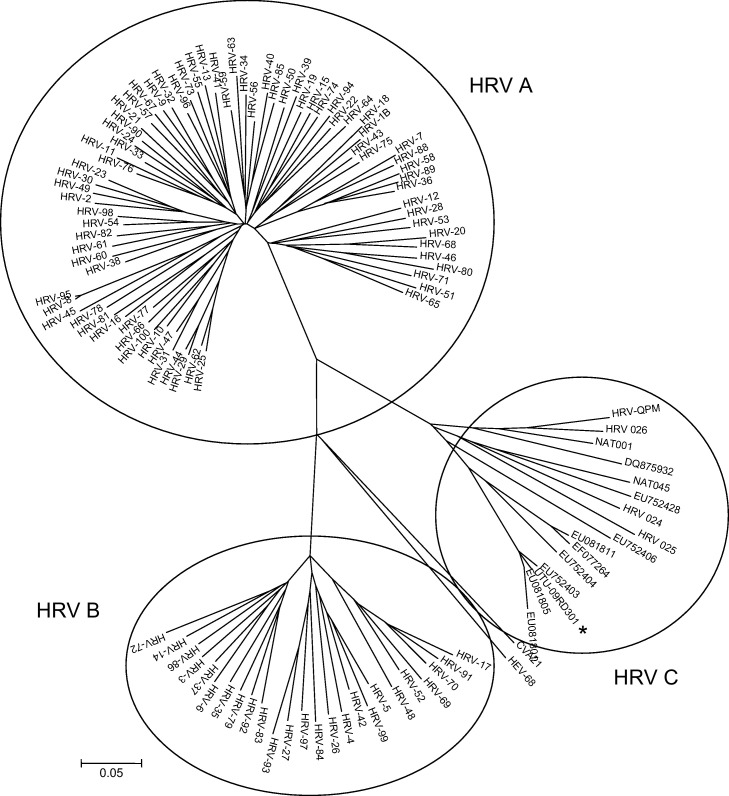
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of the VP4/2 coding region of the patient case (UTU-09RD301, GenBank accession number HQ714958) and selected published HRV sequences. For the HRV C cluster, the GenBank numbers of the partial sequences are shown. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1000 replicates is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 50% bootstrap replicates were collapsed. Virus sequences with >98% nucleotide identities were considered same. Coxsackievirus A 21 and HRV-68 sequences were used as outgroups.