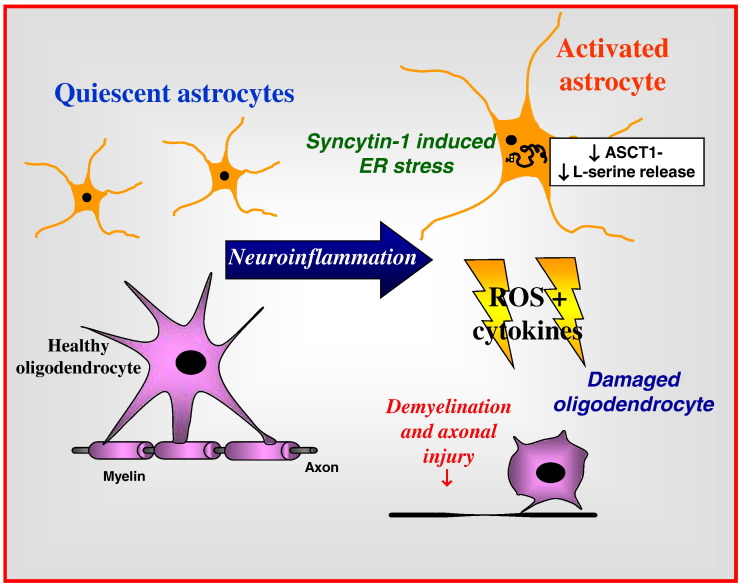
Fig. 3.
Syncytin-1-mediated neuropathogenesis in multiple sclerosis. Inflammation induces expression of syncytin-1 in astrocytes (and microglia), resulting in the release of cytokines and free radicals together with altered transport of amino acids implicated in neuropathogenesis including L- and D-serine, cysteine due to altered ASCT1 expression on astrocytes, which damage oligodendrocytes leading to demyelination and axonal injury.