Fig. 5.
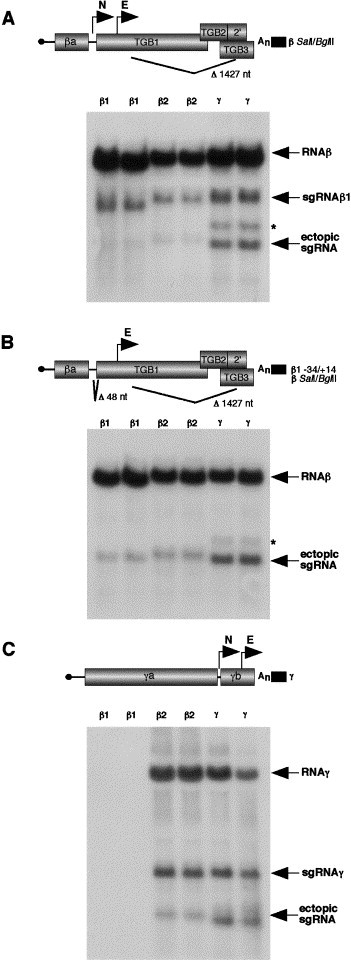
Ectopic expression of the sgRNAγ, sgRNAβ1, and sgRNAβ2 promoters in RNAβ and RNAγ derivatives. The designations on the genomic RNAs are as described in the legend to Fig. 1. N and E represent the native promoters and the ectopic promoter insertion sites, respectively. Protoplast transfections and RNA blots were carried out as described in Fig. 2. (A) Activity of the 150 nt sgRNAβ1 (β1), 294 nt sgRNAβ2 (β2), and 275 nt sgRNAγ (γ) fragments inserted at nt 1134 of the β S/B (β SalI/BglII) RNA containing the native sgRNAβ1 promoter. Duplicate tubes of BY2 protoplasts were transfected with RNAs α and γ, and either the βS/B+150 nt sgβ1, the βS/B+sgβ2, or the βS/B+sgγ RNA derivatives. RNA blots were probed with a β-specific riboprobe (βc-2785). (B) Expression of the sgRNAβ1, sgRNAβ2, and sgRNAγ promoters in the RNAβ S/B derivative (β1−34/+14), which contains a 48-nt deletion inactivating the native sgRNAβ1 promoter. (C) Activity of the sgRNAβ1, sgRNAβ2, and sgRNAγ promoters inserted into the γb ORF at nt 2339 of RNAγ. Protoplasts were coinoculated with RNAα and RNAγ containing the promoter fragments and extracted at 20 hpi. RNA blots were probed with a riboprobe that anneals to the conserved 3′ end of BSMV RNAs and therefore should detect all genomic and sgRNAs. Asterisks along the side of A and B refer to a consistently observed band of unknown origin that originated from the sgRNAγ promoter insertions.
