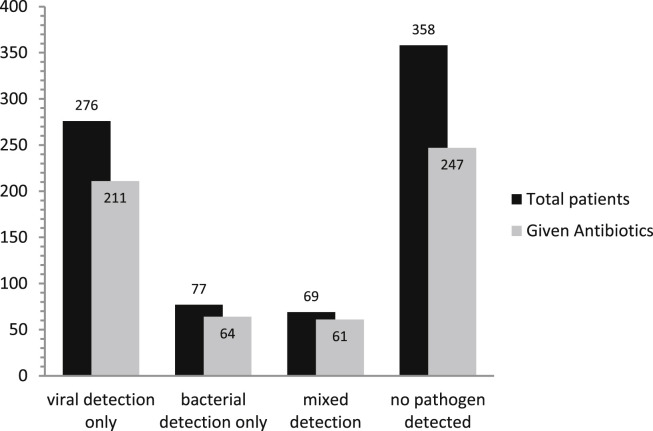
Figure 1.
Antibiotic use in patients by detected aetiology from a study of hospitalised adults with acute respiratory illness (n = 758). Mixed detection refers to the concurrent detection of viruses and bacteria in the same patient.
[Reproduced from: Clark TW, et al. Adults hospitalised with acute respiratory illness rarely have detectable bacteria in the absence of COPD or pneumonia; viral infection predominates in a large prospective UK sample. J Infect 2014;69(5):507–15].