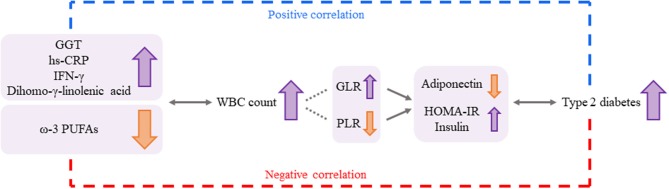
Figure 4.
A possible association among the independent predictors for changes in WBC levels, the WBC count, and the risk for type 2 diabetes. GGT, hs-CRP, IFG-γ, ω-3 PUFAs, and dihomo-γ-linolenic acid could be considered independent predictors for changes in WBC levels, and the altered WBC levels were associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes by having relationships with glucose-related markers (adiponectin, HOMA-IR, and insulin). Changes in GLR and PLR according to WBC levels can underpin these associations more strongly. Thus, the independent predictors (inflammatory markers and plasma FAs) may have a potential role in increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes by elevating WBC levels. GGT: γ-glutamyltransferase. GLR, granulocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IFN, interferon; PLR, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; WBC, white blood cell.