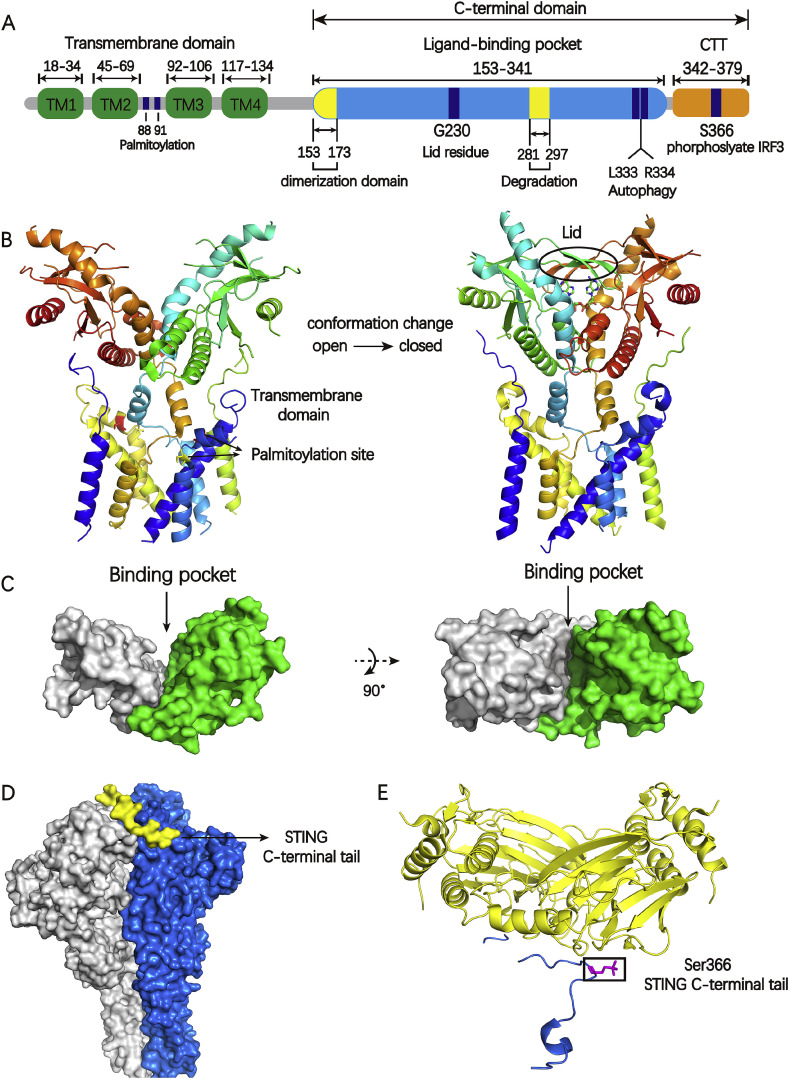
Fig. 2.
A) The schematic of human STING domain organization; B) The left is the full-length of apo human STING in open conformation (PDB code: 6NT5) and the right is chicken STING with cGAMP in a closed conformation (PDB code: 6NT7). The Cys 88 and Cys 91 in transmembrane domain is palmitoylated which may further promote STING oligomerization and subsequent activation of TBK1, colored green and yellow respectively. The appearance of lid region is the feature of closed conformation; C) The globular C-terminal domain of human STING with a large binding pocket (PDB code: 4F9G); D) The densities for the two protomers of the TBK1 dimer are colored gray or blue. The densities for the two STING C-terminal tails are colored yellow (PDB code: 6NT9); E) Phosphorylated STING C-terminal tail in complex with IRF3, colored blue and yellow, respectively. The residue S366(magenta) in STING C-terminal tail is required for STING to be licensed for the interaction with IRF3 (PDB code:5JEJ). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)