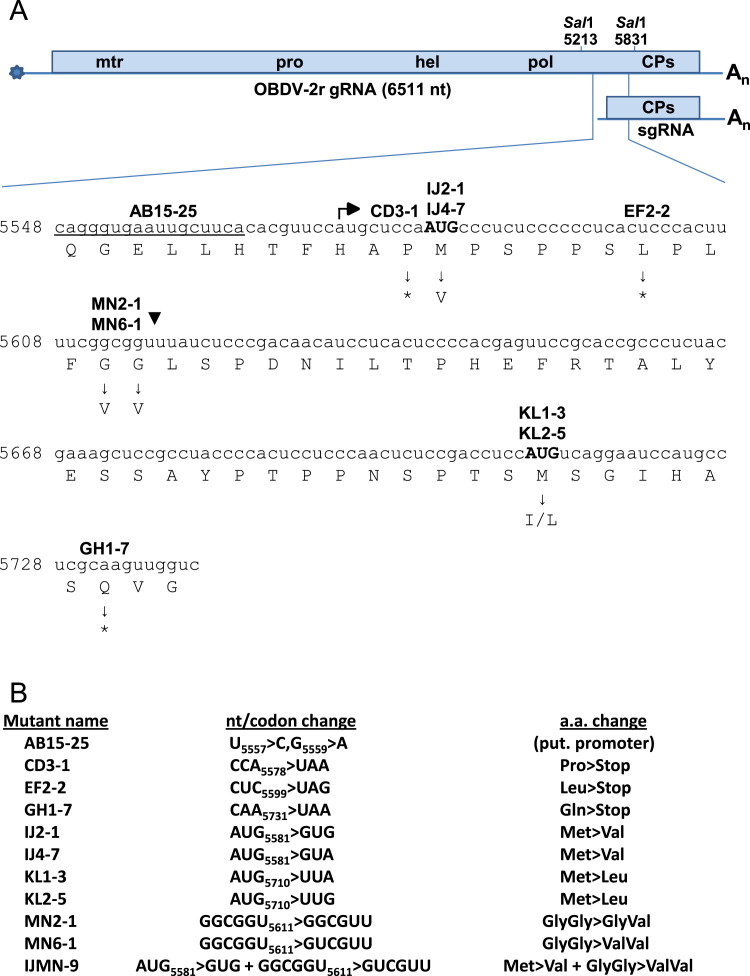
Fig. 1.
Illustration of the OBDV genome, and the genomic region and mutants used in the investigation of coat protein (CP) expression. (A) Diagram of the OBDV genome and the nucleotide sequence in the region encoding the CPs. The genomic RNA possesses a 5' cap structure (star) and a 3'-poly A tail (An). The single, large ORF encodes a polyprotein with domains specifying methyltransferase (mtr), protease (pro), helicase/NTpase (hel), and polymerase (pol) activities fused to the sequence encoding the CPs. The major and minor coat proteins map to the same CP sequence and size differences between them are potentially determined by translation initiation at two different start codons (minor, AUG5581 and major, AUG5710). Whereas the major CP is postulated to be translated primarily from sgRNA, the minor CP could be produced by translation directly from the sgRNA, by cleavage after Gly–Gly(▼) of either or both the large polyprotein or a protein initiated at AUG5581, or by both direct translation and cleavage. The putative promoter for sgRNA synthesis, the marafibox, is underlined and the start site for sgRNA synthesis (this work) is indicated by the bent arrow. Sites where premature termination codons were introduced are indicated by asterisks. Mutant names are shown above the corresponding sequence locations, and amino acid changes in potential initiation and protease cleavage site codons are shown under the sequence. (B) Mutant description and nomenclature. The mutant name is followed by indication of nucleotide/codon substitutions and the cognate amino acid change. Mutant IJMN-9 represents a double mutant altering both the putative minor CP initiation codon and the potential cleavage site.