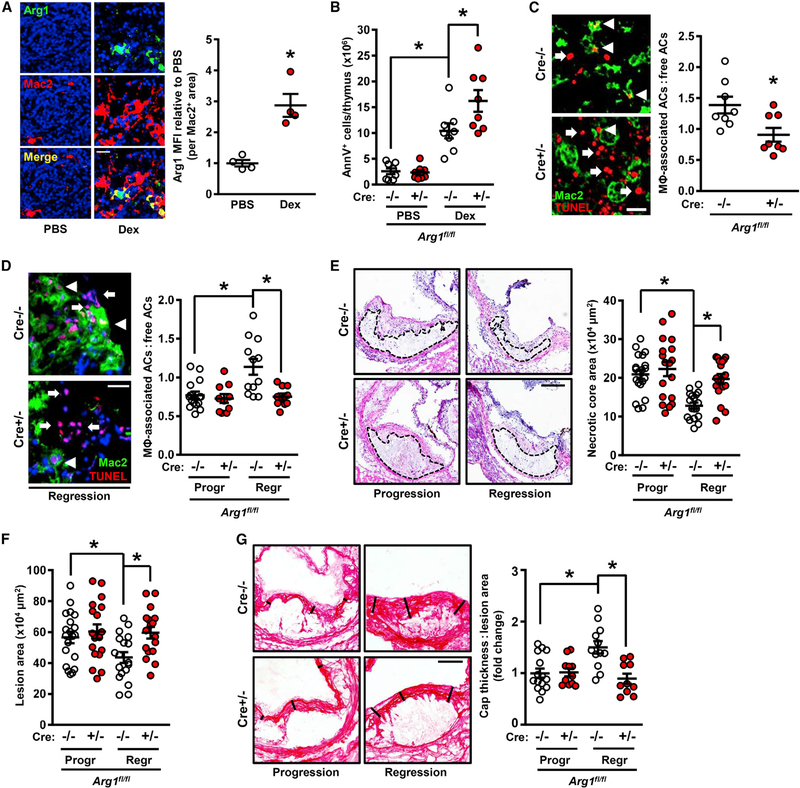
Figure 2. Myeloid-Arg1 Deletion Impairs Efferocytosis In Vivo.
(A) Arg1 immunostaining with quantification of thymic sections from mice 18 h after i.p. injection with PBS or dexamethasone (Dex) (n = 4 mice per group). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(B) Annexin V+ cells in thymi from myeloid-Arg1 WT (Cre−/−) and KO (+/−) mice harvested 18 h after injection with PBS or dexamethasone (n = 8 mice per group).
(C) Quantification of efferocytosis (macrophage-associated ACs:free ACs ratio) in thymic sections from the mice in (B) (n = 8 per group). Arrowheads and arrows depict macrophage-associated and free TUNEL+ cells, respectively.
(D–G) Arg1fl/fl Ldlr−/− (Cre−/−) and Arg1fl/fl Lysz2-Cre+/− Ldlr−/− (Cre+/−) mice placed on atherosclerosis progression (Progr) or regression (Regr) protocols were assayed for the following parameters: (D) efferocytosis (scale bar, 40 μm), (E and F) aortic root (E) necrotic core and (F) lesion areas (n = 17–20 mice per group; scale bar, 200 μm), and (G) collagen cap thickness (n = 10–15 mice per group; scale bar, 100 μm).
All values are means ± SEM; *p < 0.05; n.s., not significant.