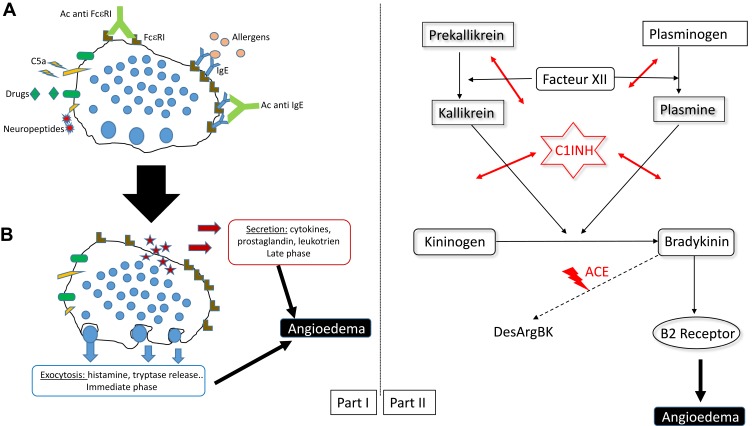
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of biochemical pathways responsible for angioedema. Part I: Mast cell angioedema. (A) Mast cell activation by different modes (allergic or non-allergic). (B) Release of various mediators responsible for angioedema. Part II: Bradykinin angioedema (kallikrein-kinin system).
Abbreviations: C1-inh, C1inhibitor; ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme.