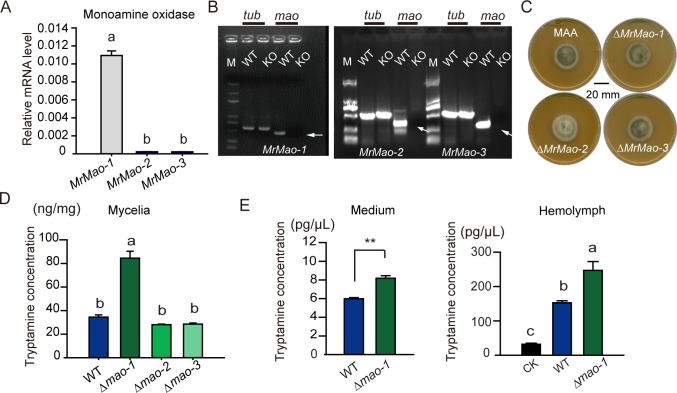
Fig 5. Deletion of MrMAO genes in MAA significantly promoted the tryptamine concentration in mutants.
(A) qRT-PCR analysis showed that MrMao-1 presented the highest level of mRNA expression in the MrMao gene family. (B) By introducing the pDHt-MAO-bar plasmid, we knocked out the MrMao genes in MAA. RT-PCR results showed that MrMao genes (MrMao-1, MrMao-2, and MrMao-3) were successfully knocked out from the MAA genome. M: DNA ladder D2000; WT: wild type of MAA; KO: MAA samples of knockout MrMao, tub: tubulin gene. White arrow indicates the target bands of Δmao strain samples. (C) The colony morphology of mutant and wild-type MAA strains showed little difference in the PDA medium. (D) HPLC analysis of the tryptamine level in the hyphae cultured in the L-15 medium with locust hemolymph supplement. The results showed that knocking out MrMao-1 increased the tryptamine level, but MrMao-2 and MrMao-3 did not affect the tryptamine level in MAA (n = 8–14, different lowercase letters indicated a significant difference at P < 0.05, WT: wild type). (E) The left panel showed the extracellular concentrations of tryptamine in the MAA strain of WT and Δmao-1. The Δmao-1 strain showed higher levels of tryptamine in the mycelia and medium than did the WT strain. The data were presented as mean ± SEM, Student’s t-test. Asterisks showed the significance at P < 0.01. WT: wild type. The right panel showed that the Δmao-1 strain infection induced a higher level of tryptamine in the hemolymph of locust than did the WT strain by HPLC analysis. CK: mock control (n = 10, different lowercase letters indicated significance at P < 0.05).