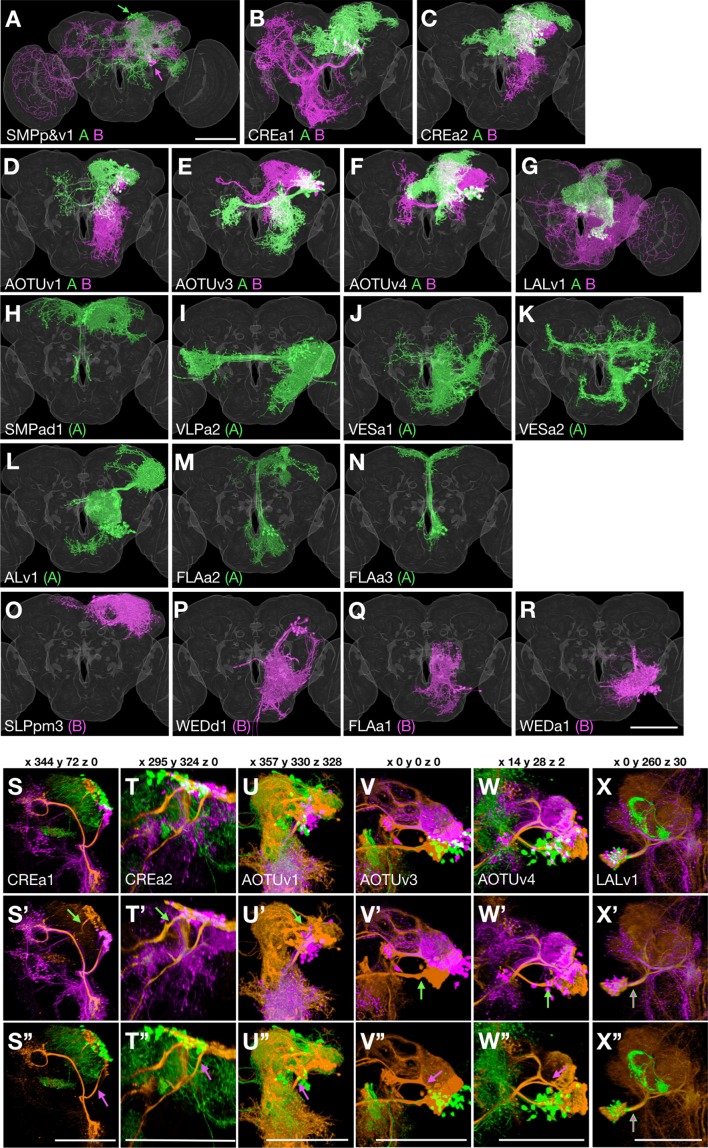
Figure 2. Sister hemilineage distinctions.
(A–R) Hemilineage morphology is revealed by pseudo-coloring Non/A neurons green and Noff/B neurons magenta based on the Notch state (judged from notch RNAi phenotypes). For the seven Vnd lineages composed of dual hemilineages (A–G), representative single-cell clones of A or B neurons were assembled to create synthetic NB clones with sister hemilineages in distinct colors. For the 11 unpaired Vnd hemlineages (H–R), the full pattern was shown by merging the first larval-born neuron with its accompanying NB clone and then pseudo-coloring the merged clone according to A/B fate. (S–X’’) Full-size NB clones (orange) overlaid with both A (green) and B (magenta) hemilineage masks (S–X) or either B (S’–X’) or A (S’’–X’’) hemilineage mask, to examine the hemilineage-structure correspondence in dual-hemilineage NB clones (except SMPp&v1 with widely separate A/B cell body clusters). Composite confocal images viewed from various angles (x, y, and z coordinates indicated above) demonstrate distinct hemilineage-specific neurite fascicles (indicated with green/magenta arrows), extending out of fully or partially separate A and B cell body clusters, in six of the seven Vnd lineages (S–W’’). Only the LALv1 lineage has a mixed cell body region that extends a single neurite bundle projecting posteriorly before dividing into multiple fascicles (X–X’’).