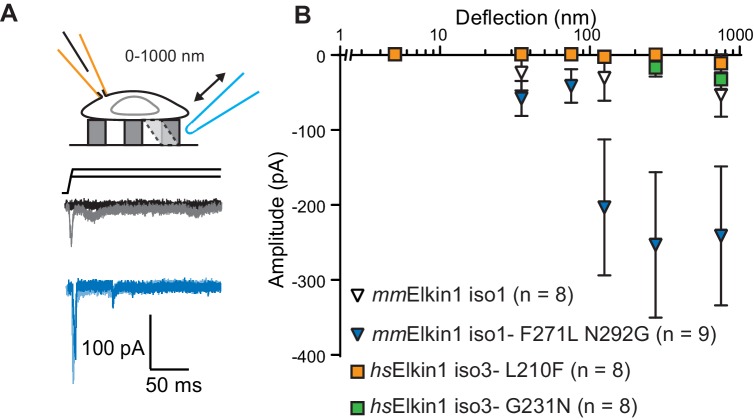
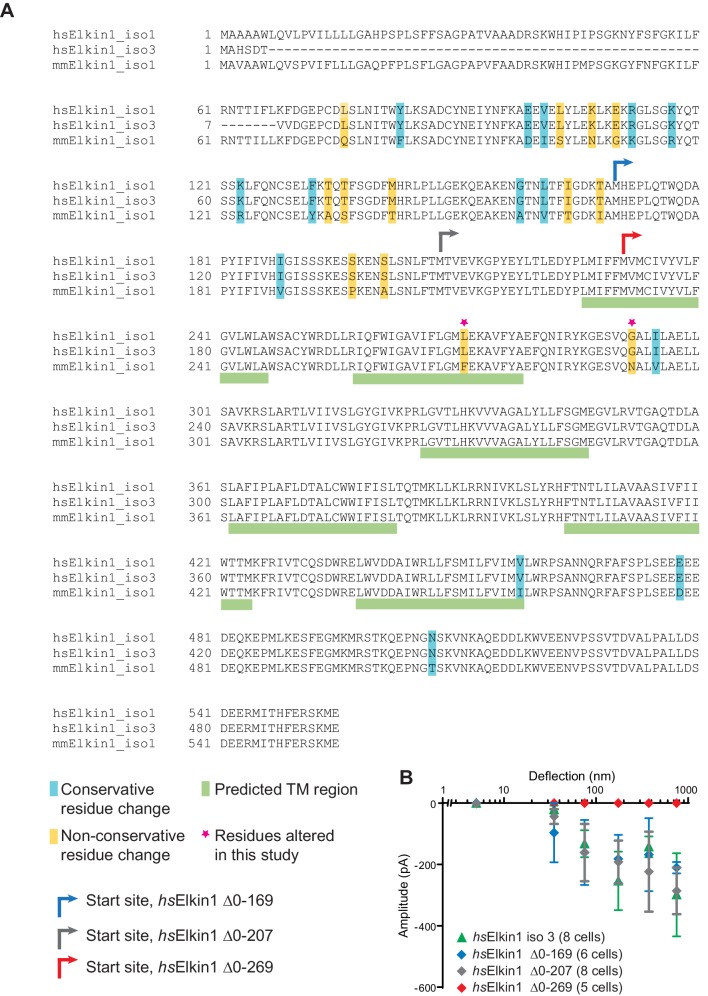
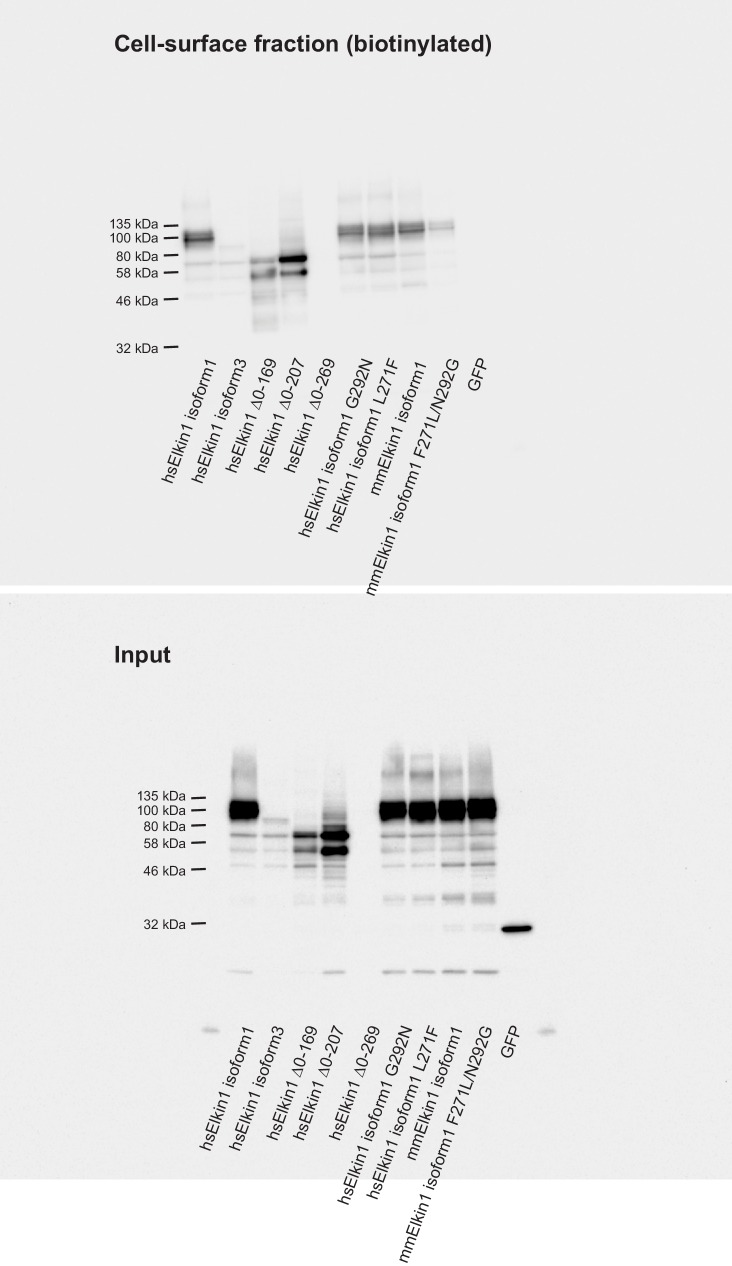
Figure 4. hsElkin1 and mmElkin1-dependent currents exhibit distinct mechano-sensitivity.
(A) Example traces of M. musculus Elkin1-dependent MA currents in HEK-293T P1KO cells (grey: mmElkin1-iso1; blue mmElkin1-iso1 F271L N292G). (B) Stimulus-response plots of HEK-293T P1KO cells expressing: mmElkin1-iso1 (open triangles, n = 8 cells), mmElkin1-iso1 F271L N292G (blue triangles, n = 9 cells), hsElkin1-iso3 L210F (orange squares, n = 8 cells), hsElkin1-iso3 G231N, (green squares, n = 8 cells). Data points presented as mean ± s.e.m. Cartoons of stimuli adapted from Rocio Servin-Vences et al. (2017). See Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for sequence alignment of hsElkin1 and mmElkin1, Figure 4—figure supplement 2 for surface biotinylation analysis of Elkin1 variants and Figure 4—source data 1 for details on current kinetics.