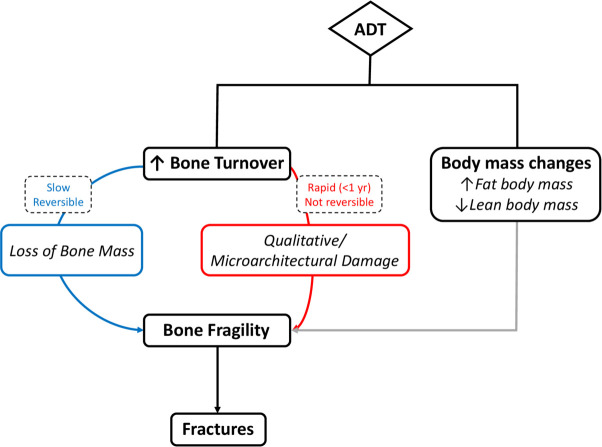
Figure 1.
ADT-induced bone impairment. ADT augments bone fragility, and thus the risk of fracture, through two mechanisms: (1) bone turnover increase, which leads to bone mass loss via a slow, reversible process, and to qualitative/microarchitectural alterations via a rapid, non-reversible mechanism; (2) body mass changes, namely increased fat body mass and decreased lean body mass. ADT, androgen-deprivation therapy.